lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2/let-7a-5p axis regulates metabolic reprogramming by targeting HK2 in oral submucous fibrosis-associated oral squamous cell carcinoma


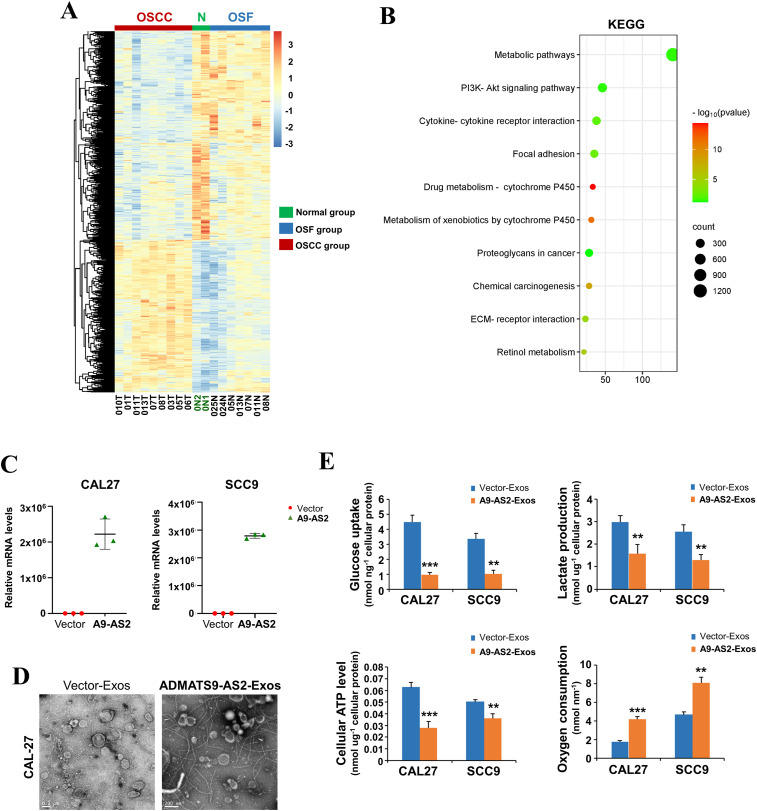
Oral squamous cell carcinoma in the background of/with oral submucous fibrosis (OSCC-OSF) has a unique etiology and is clinically distinct from other OSCCs. We previously identified ADAMTS9-AS2 as a functional tumor suppressor in OSCC-OSF through the regulation of PI3K-AKT signaling. However, its role in metabolic modulation and the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. In this study, we reported for the first time that ADAMTS9-AS2 suppressed aerobic glycolysis by cooperating with let-7a-5p in OSCC cells. Mechanistically, let-7a-5p inhibited HK2 expression by targeting its 3′-UTR, further deregulating glycolytic function, while enhancing HK2 expression rescued the inhibitory effects of the ADAMTS9-AS2/let-7a-5p axis on aerobic glycolysis and OSCC cell growth. Exosomal ADAMTS9-AS2 regulated metabolic reprogramming during OSCC tumorigenesis. ABC transporters in lipid and pyrimidine metabolism were significantly enriched pathways. Changes in several key metabolites were identified after ADAMTS9-AS2 exosome treatment, including increased levels of DL-glutamic acid and D-mannose, along with decreased levels of cytidine and D-maltose. Thus, our findings demonstrate that ADAMTS9-AS2 drives let-7a-5p binding to HK2 to suppress cell growth in OSCC by abolishing aerobic glycolysis. Our data on metabolic reprogramming have greatly expanded the role of the ADAMTS9-AS2/let-7a-5p axis as a key regulator of metabolism during OSCC tumorigenesis.