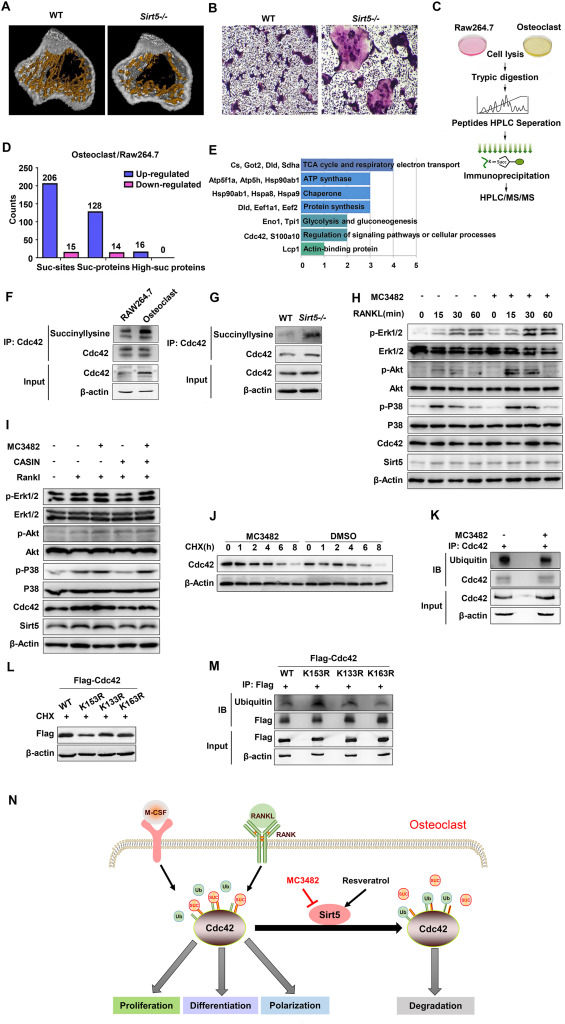
Sirt5 desuccinylates Cdc42 to mediate osteoclastogenesis and bone remodeling in mice


Post-translational modifications (PTMs) play a critical role in bone remodeling, with phosphorylation and acetylation being particularly well characterized. Recently, succinylation, a relatively uncommon PTM on lysine, has received considerable research attention for its influence on several physiological and pathological processes and conditions.1 Several substrates involved in mitochondrial pathways have been validated as substrates for the desuccinylase sirtuin 5 (Sirt5), a key regulator of succinylation.2 Bone is one of the most metabolically active organs, but the role of succinylation during bone remodeling is not well characterized.