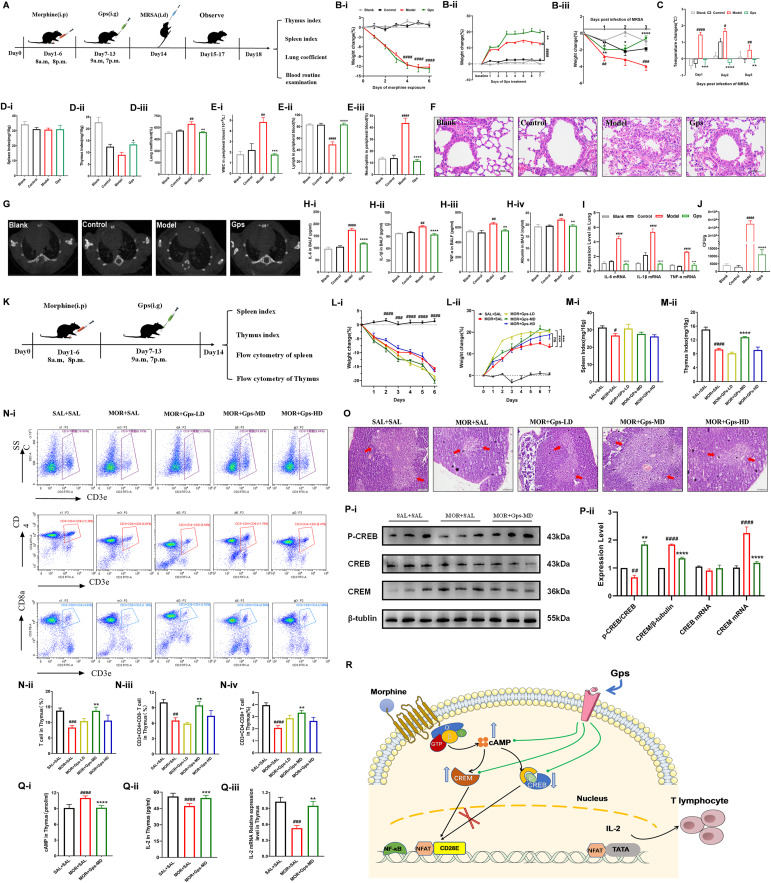
Gypenosides ameliorate morphine-induced immunosuppression with an increased proportion of thymic T lymphocyte subsets and are involved in the regulation of the cAMP-CREM/CREB-IL-2 pathway


Opioid abuse can suppress the lymphatic system function, and produce severe immunosuppression that poses a significant risk of opportunistic infections such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) pneumonia.1,2 Gypenosides (Gps) are the most important immunomodulator components in the Chinese herbal medicine Gynostemma pentaphyllum.3 However, the immunomodulatory mechanism and effect of Gps on morphine-induced immunosuppression are still unknown. We aimed to investigate the pharmacological effects of Gps in morphine-induced immunosuppressive mice and the underlying mechanism involved.