Curcumin modulates oxidative stress to inhibit pyroptosis and improve the inflammatory microenvironment to treat endometriosis


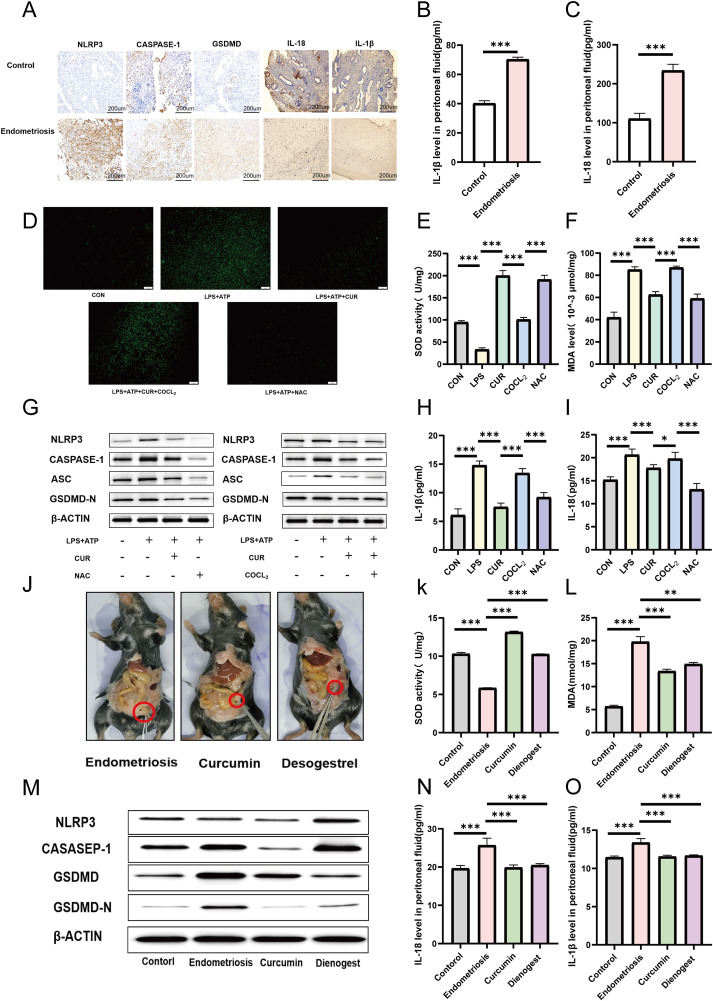
Endometriosis (EM) is a common disease that affects approximately 10%–15% of women of childbearing age. The pathogenesis of EM is unclear, but studies have shown a strong association between EM and inflammation, as well as oxidative stress.1 Pyroptosis is also called inflammatory cell death. When pyroptosis occurs, it activates a strong inflammatory response. Pyroptosis is associated with oxidative stress, and ROS act as intermediate triggers to activate pyroptosis, which can exacerbate the subsequent inflammatory cascade.2 However, it is unknown whether pyroptosis is regulated by oxidative stress during EM. Curcumin (CUR) is one of the world's best-selling natural food colorants and has a variety of pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, and the pharmacological effects of CUR are associated with the mechanisms of pyroptosis and EM.3,4 In the present study, we showed that CUR ameliorated the inflammatory environment of EM by modulating oxidative stress and inhibiting GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis involving the NLRP3 inflammasome. These results further confirm the inflammation and oxidative stress theory of EM and provide new drug options for EM treatment.