Efficacy of rapid antigen self-testing for SARS-CoV-2 screening: Real-world evidence from a prospective cohort study


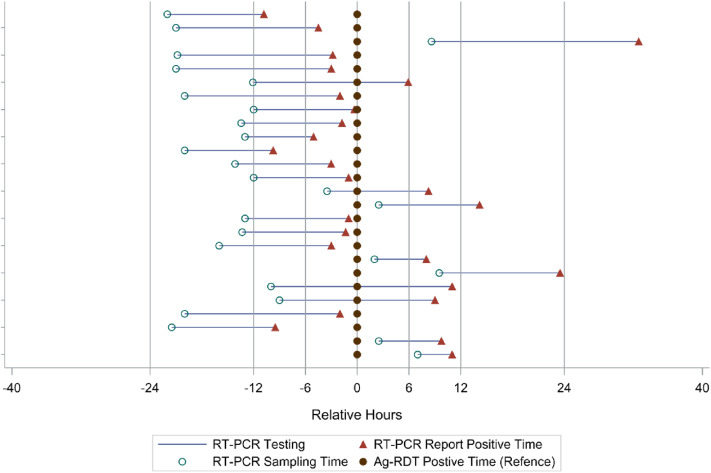
Antigen rapid diagnostic tests (Ag-RDTs) have been considered and implemented as an important diagnostic and screening tool to identify SARS-CoV-2 infections in community settings.1 Ag-RDTs are less sensitive, particularly in asymptomatic populations, compared with laboratory-based viral nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) such as reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).2 However, taking into account the facts that Ag-RDTs are effective for identifying most contagious individuals, they are faster and less expensive than RT-PCR, as well as that RT-PCR could produce positive results for weeks to months after the infection,2 WHO recommends Ag-RDTs be offered as COVID-19 self-testing for screening purposes in addition to professionally administered testing services regardless of the community transmission level.1 Although Ag-RDTs have been utilized in mass screening in Slovakia and Liverpool,2 there is a dearth of real-world evidence from prospective cohort studies on the efficacy of Ag-RDT self-testing in comparison to RT-PCR due to the challenges in performing both testing consecutively at the same time over the follow-up. The study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of rapid antigen self-testing for screening SARS-CoV-2.