Simultaneous detection of methylation and genetic variations of BCR-ABL1 gene by nanopore Cas9-targeted sequencing


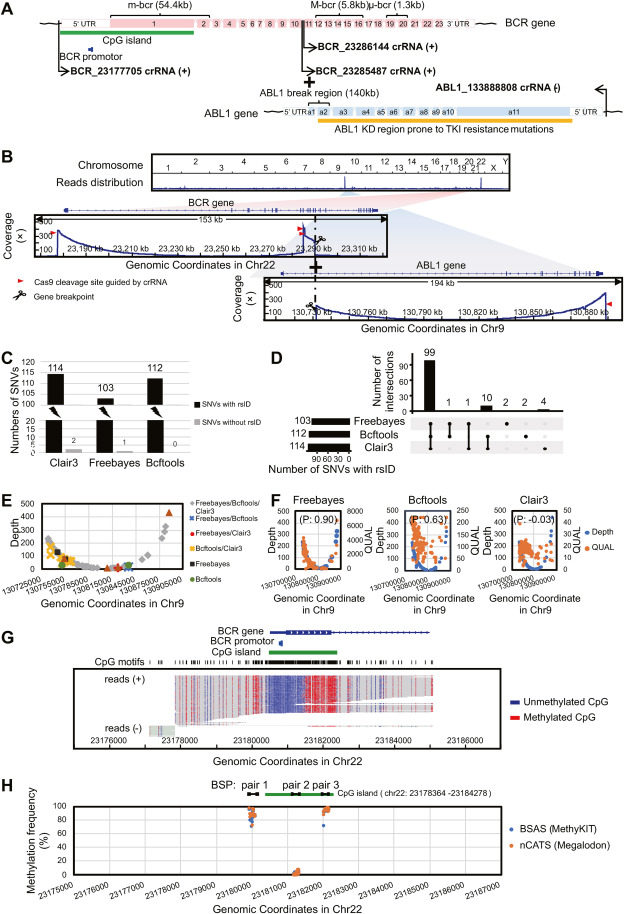
The BCR-ABL1 fusion gene is a driver and hallmark of leukemia and a classic structural variant.1 Single nucleotide variations (SNVs) occurring in the ABL1 gene kinase domain (KD)2 and aberrant DNA methylation modifications, specifically 5-methylcytosine (5mC) of the BCR gene promoter,3 have strong clinical implications, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance, therapeutic responsiveness, and disease progression. Therefore, detecting the presence of KD region mutations and/or promoter 5mC modifications in the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene may help clinicians formulate individualized treatment regimens for patients with leukemia. Currently, the clinical detection of structural variants, SNVs, and 5mC modifications relies on a variety of independent techniques, and comprehensive techniques that can simultaneously detect all three events in one assay are urgently needed. Here, we report the direct detection of all three events using nanopore Cas9-targeted sequencing (nCATS),4 which combines Cas9-mediated target enrichment and the advantages of long-read length and direct sequencing of the Oxford Nanopore Technologies platform.