PDLIM1 sustains DNA damage response by promoting chromatin relaxation and activating DNA–PK complex


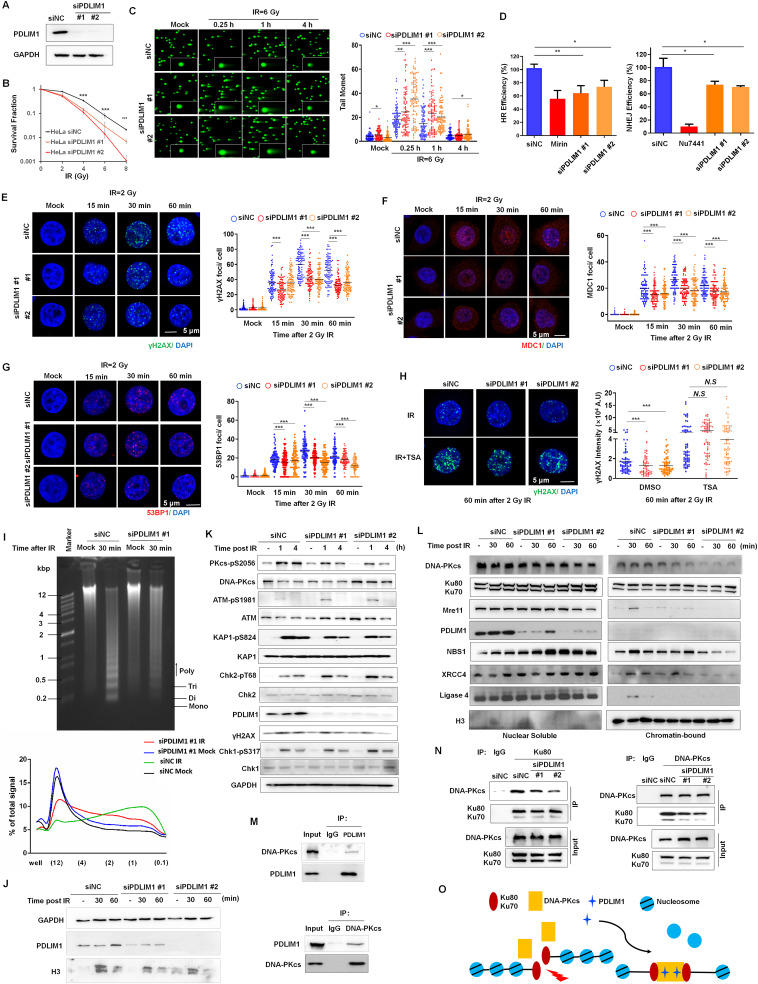
PDZ and LIM domain protein 1 (PDLIM1) is a cytoplasmic LIM protein that regulates cytoskeleton organization and functions as a platform to coordinate various cellular processes.1 Accumulated evidence suggests that PDLIM1 plays important roles in tumorigenesis, tumor progression, and response to cancer therapy. Consistently, our results demonstrated that silencing PDLIM1 significantly inhibited the migration and the invasion of HeLa cells compared with control cells (Fig. S1). However, the feasibility of targeting PDLIM1 as an effective strategy for radiotherapy remains to be determined. Here, we knocked down PDLIM1 while irradiating with 60Co γ-rays (IR), and impaired clonogenic survival was observed in PDLIM1-depleted HeLa cells (Fig. 1A, B). Furthermore, the heightened radiosensitivity prompted by PDLIM1 knockdown was effectively counteracted through the expression of siRNA-resistant PDLIM1 protein (Fig. S2A, B). To determine whether PDLIM1 affects DNA damage repair following IR exposure, we performed a neutral comet assay. PDLIM1 knockdown cells have significantly more unrepaired IR-induced DNA double strands breaks (DSBs) compared with control cells, as monitored by comet tail moment (Fig. 1C). There are two primary mechanisms for the restoration of DNA DSBs: homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). Therefore, the quantitative assessment of NHEJ and HR efficiencies was conducted in vivo using a CRISPR/Cas9-mediated oligodeoxynuceotide (ODN) detection system.2 The loss of PDLIM1 significantly reduces both NHEJ and HR activity within HeLa cells (Fig. 1D). Subsequently, HeLa cells were subjected to IR, followed by immunofluorescence staining targeting γH2AX, which represents a prominent chromatin modification trigger by several phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related family members after DNA DSBs. Interestingly, the depletion of PDLIM1 substantially abrogated the formation of γH2AX after IR exposure (Fig. 1E). The recruitment of mediator of DNA damage checkpoint protein 1 (MDC1) by γH2AX is recognized as the initial step in which the site of a DSB undergoes preparation for the activation of DNA damage response (DDR). Immunofluorescence staining also revealed that IR-induced MDC1 foci formation was attenuated in PDLIM1-deficient cells at the early time points post-IR compared with control cells (Fig. 1F). Furthermore, the hypothesis proposing that the recruitment of DDR factors to DNA DSBs necessitates the presence of PDLIM1 was further substantiated by the observation that the localization of 53BP1 (Fig. 1G) and BRCA1 (Fig. S2C) — both critical factors in NHEJ and HR pathway, respectively — at DSBs sites was diminished in cells depleted of PDLIM1, as compared with the control cells.