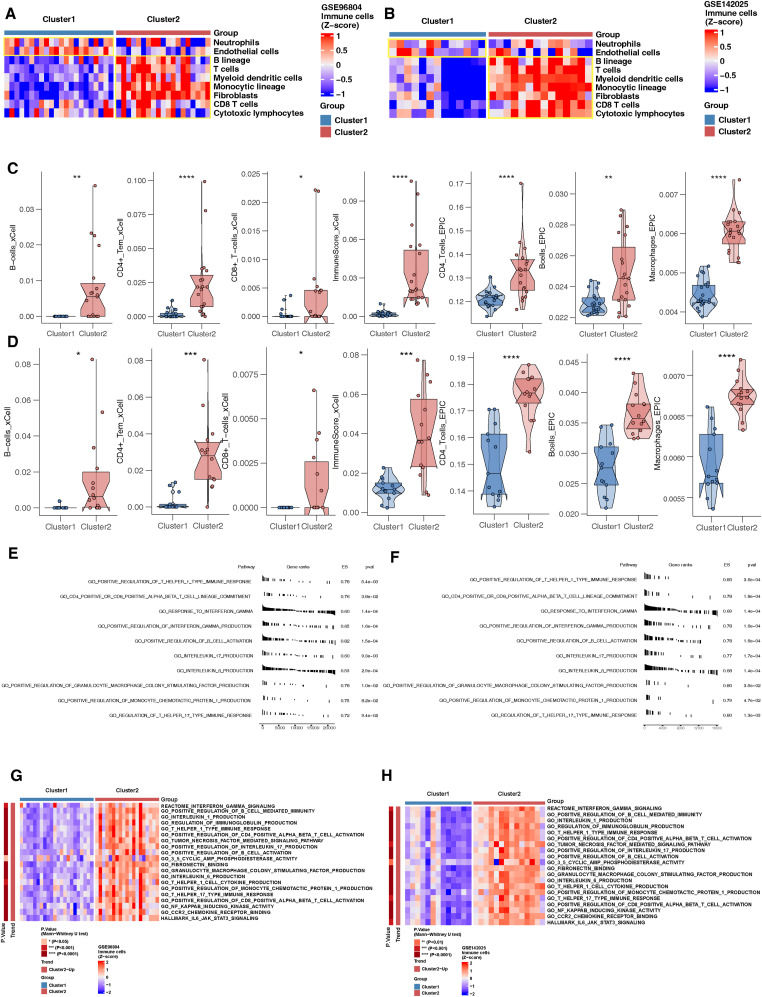
Identification of immune cell infiltration pattern in diabetic nephropathy


Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is now the most common cause of end-stage renal disease in the world. Inflammatory and immune responses play an important role in the pathogenesis of DN, but the specific mechanisms responsible for the development of this disease have yet to be fully elucidated. Numerous epidemiological and preclinical studies have shown that inflammatory response and immune response play an important role in the early stages of DN pathogenesis.1 Still, the exact mechanism for the development of this disease has not been fully elucidated.