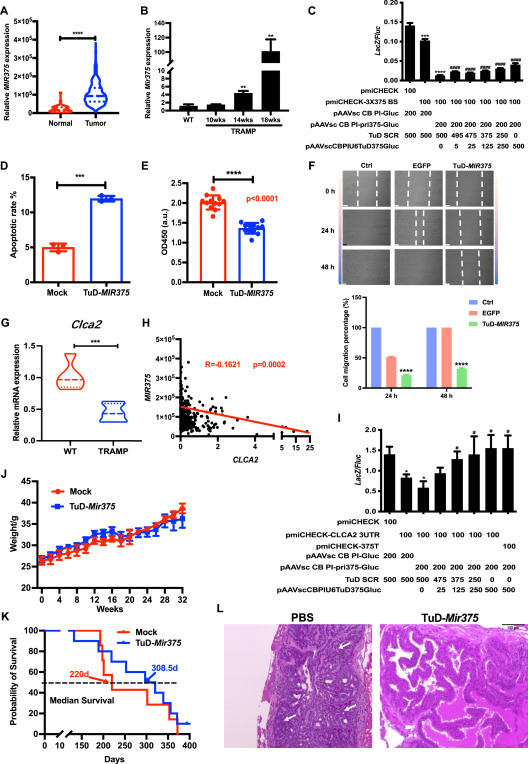
Adeno-associated virus-mediated intraprostatic suppression of MIR375 inhibits tumor progression in the TRAMP mouse model of prostate cancer


The treatment of prostate cancer (PCa) needs to be improved.1 Micro-RNAs (miRNAs) are a subtype of non-coding, single-stranded RNAs that influence cellular survival and death by modulating mRNAs. Among these miRNAs, MIR375 has a critical role in the regulation of tumorigenesis2 and holds promise as a novel therapeutic target for future PCa treatment. Recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) exhibits non-pathogenicity, low-grade inflammation, and robust and long-lasting expressions of target genes. We have previously described the rAAV9 as a valid vector to transfer target miRNAs and genes,3 so rAAV9 could be used as a vector to deliver MIR375 into the mouse prostate and PCa cells.