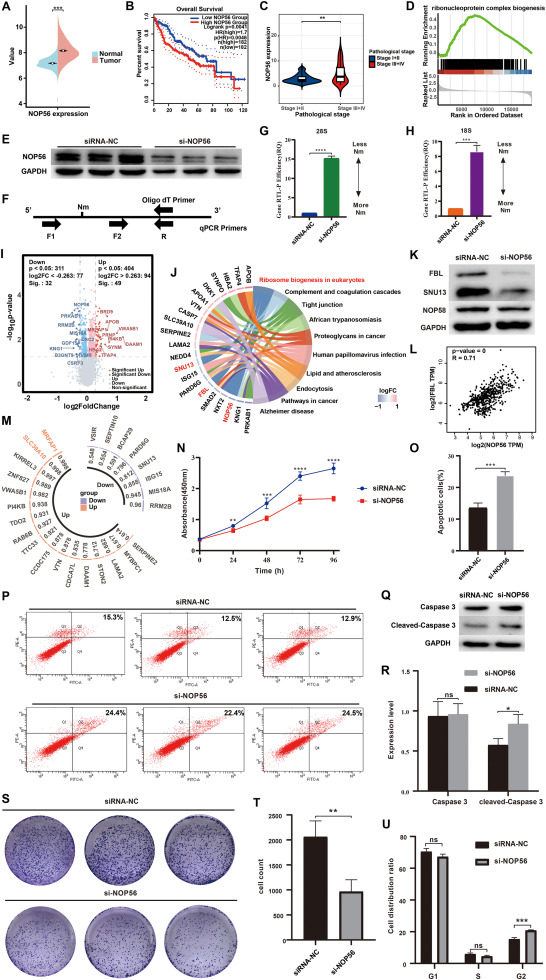
NOP56 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through 2′-O-methylation


Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common malignant tumor and one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths, with the fourth-highest incidence rate and the second-highest mortality rate in China.1 Currently, HCC is treated by surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Despite advances in treatment, the prognosis of HCC remains poor, and research on the discovery of novel drug targets is continuously needed.2