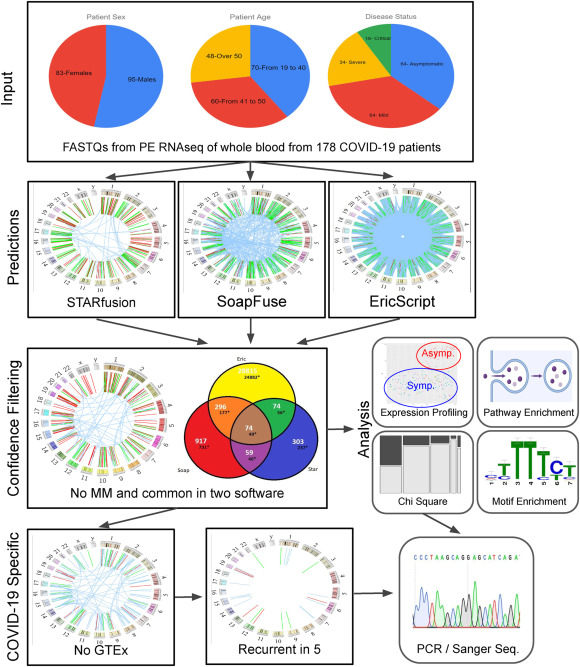
Landscape of chimeric RNAs in COVID-19 patient blood


Despite the availability of efficacious vaccines, COVID-19 persists and our knowledge of how SARS-CoV-2 infection affects host transcriptomics remains incomplete. Transcriptome analysis, which has progressed our understanding of the patient response to SARS-CoV-2 infection, can be enhanced by considering chimeric transcript expression. Here we assess and characterize chimeric RNAs found in the whole blood of 178 COVID-19 patients. STAR-Fusion, SOAPfuse, and EricScript were used to detect chimeric RNAs resulting in over 30,000 predictions with approximately 500 high-confidence predictions that were found by more than one software and filtered based on exon annotations around the chimeric splice junction. GO term enrichment performed on the 5′ and 3′ parental genes of chimeric RNAs found in severe and critical patients resulted in pathways known to be affected in these patients, such as erythroid differentiation. Motif enrichment analysis of sequences proximal to chimeric splice junctions found in COVID-19 patients versus those found in GTEx whole blood revealed two RNA binding proteins previously implicated with coronavirus infection, PTBP1 and SFPQ. We discovered a chimeric RNA that correlated with COVID-19 disease status and appeared to be dependent upon a loss of PTBP1's function as a splicing repressor. Overall, we found over 350 novel COVID-19-specific chimeric RNAs not detectable in GTEx whole blood that may also serve as biomarkers for viral infection.