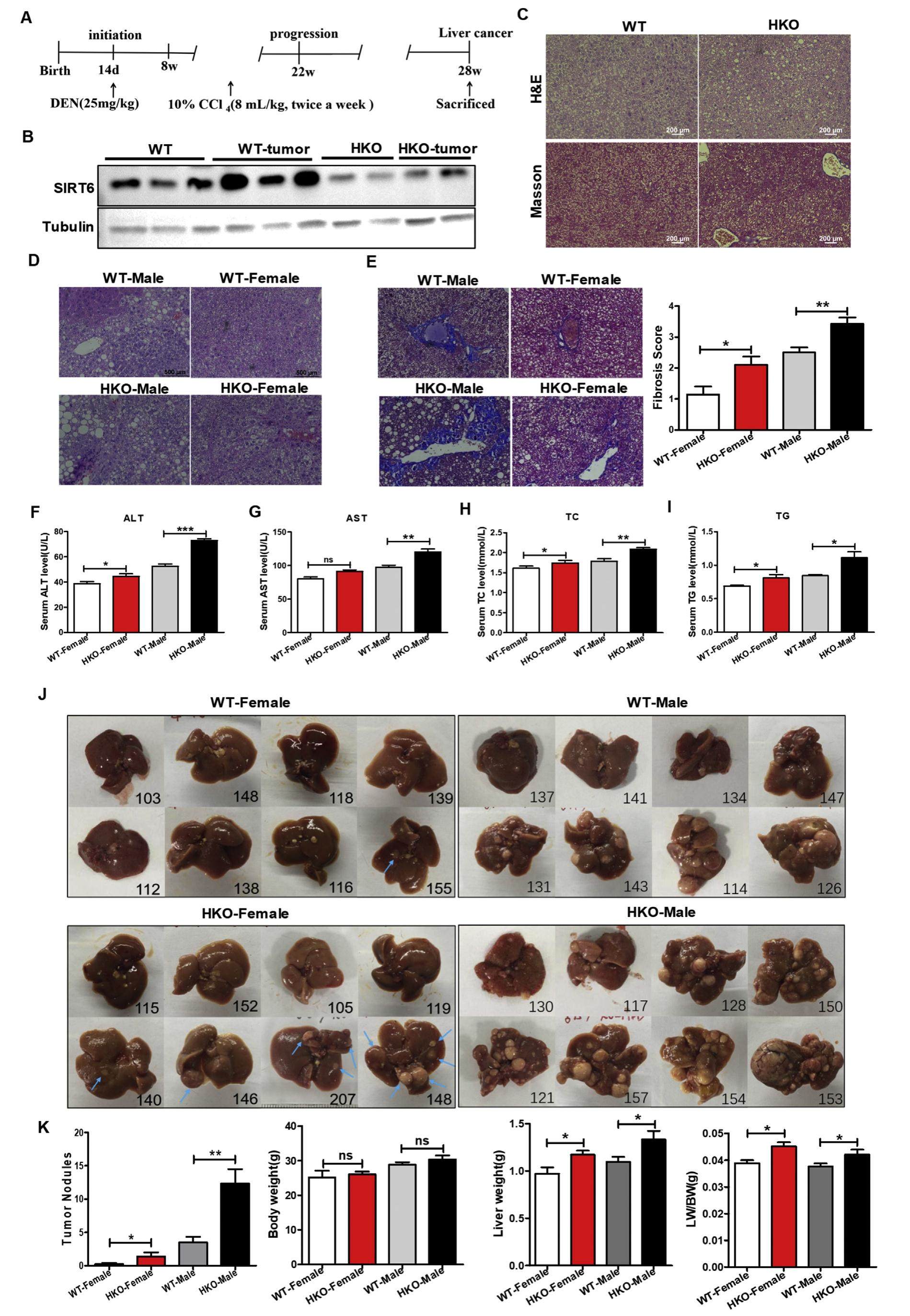
Hepatic SIRT6 deficit promotes liver tumorigenesis in the mice models


SIRT6 belongs to class III sirtuin family with NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase activities and controls multiple processes including aging, metabolism and inflammation. In recent years, increasing studies showed tumor suppressor role of SIRT6 in HCC development. We established a two-stage DEN followed CCl4 induced liver carcinogenesis in the hepatic-specific SIRT6 HKO mice models and found that hepatic SIRT6 deficit significantly promotes liver injury and liver cancer through inhibition of the ERK1/2 pathway. SIRT6 was compensatory upregulated in mice tumor tissues and human HCC cells and overexpressed SIRT6 inhibits tumor growth both in vitro and in vivo. Taken together, we provide a useful mouse model for delineating the molecular pathways involved in chronic liver diseases and primary liver cancer and suggest that SIRT6 can be a promising target for HCC therapies.