Oxidative stress and mitochondrial transfer: A new dimension towards ocular diseases


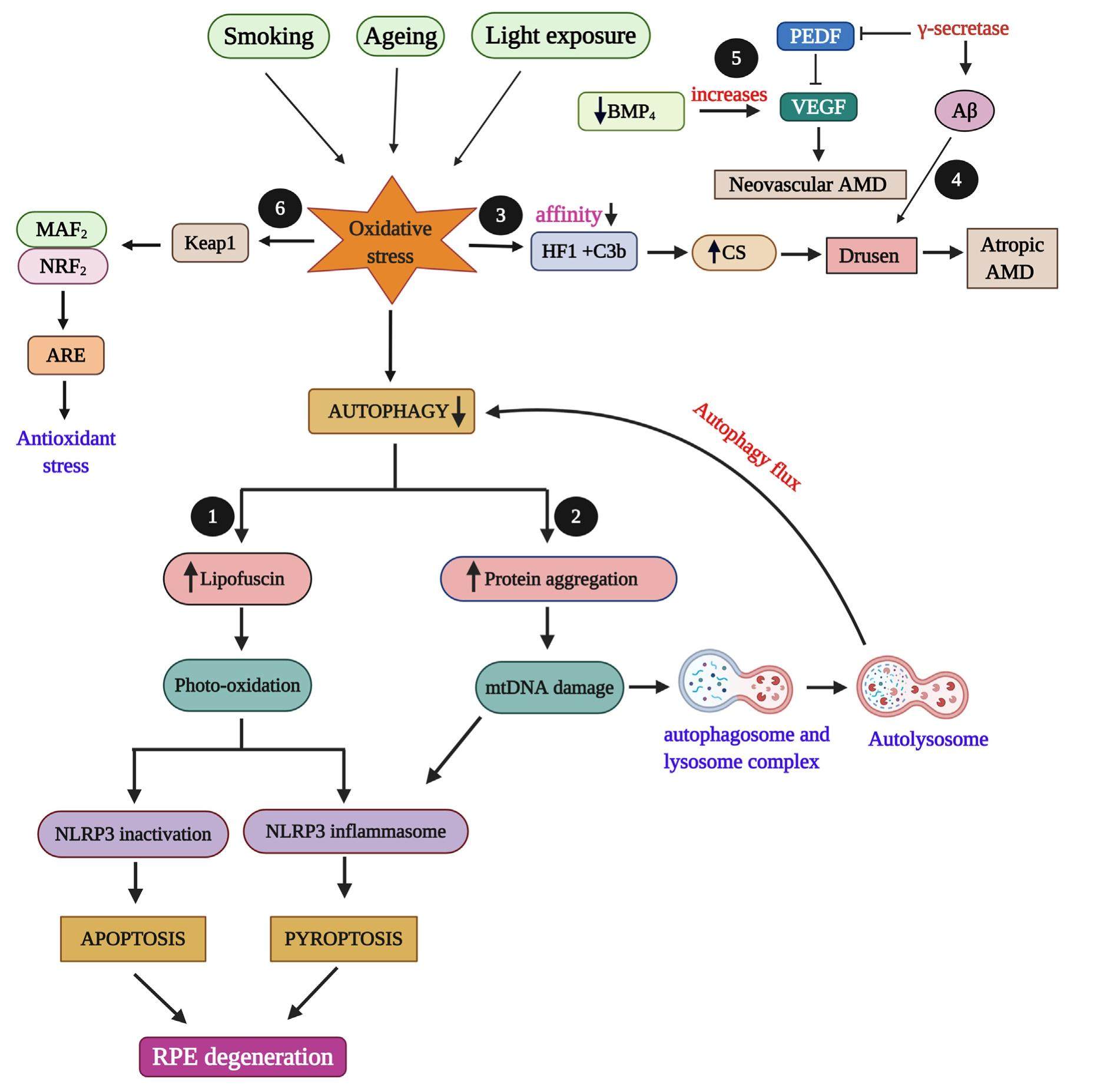
Ocular cells like, retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is a highly specialized pigmented monolayer of post-mitotic cells, which is located in the posterior segment of the eye between neuro sensory retina and vascular choroid. It functions as a selective barrier and nourishes retinal visual cells. As a result of high-level oxygen consumption of retinal cells, RPE cells are vulnerable to chronic oxidative stress and an increased level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated from mitochondria. These oxidative stress and ROS generation in retinal cells lead to RPE degeneration. Various sources including mtDNA damage could be an important factor of oxidative stress in RPE. Gene therapy and mitochondrial transfer studies are emerging fields in ocular disease research. For retinal degenerative diseases stem cell-based transplantation methods are developed from basic research to preclinical and clinical trials. Translational research contributions of gene and cell therapy would be a new strategy to prevent, treat and cure various ocular diseases. This review focuses on the effect of oxidative stress in ocular cell degeneration and recent translational researches on retinal degenerative diseases to cure blindness.