Ccrl2 deficiency deteriorates obesity and insulin resistance through increasing adipose tissue macrophages infiltration


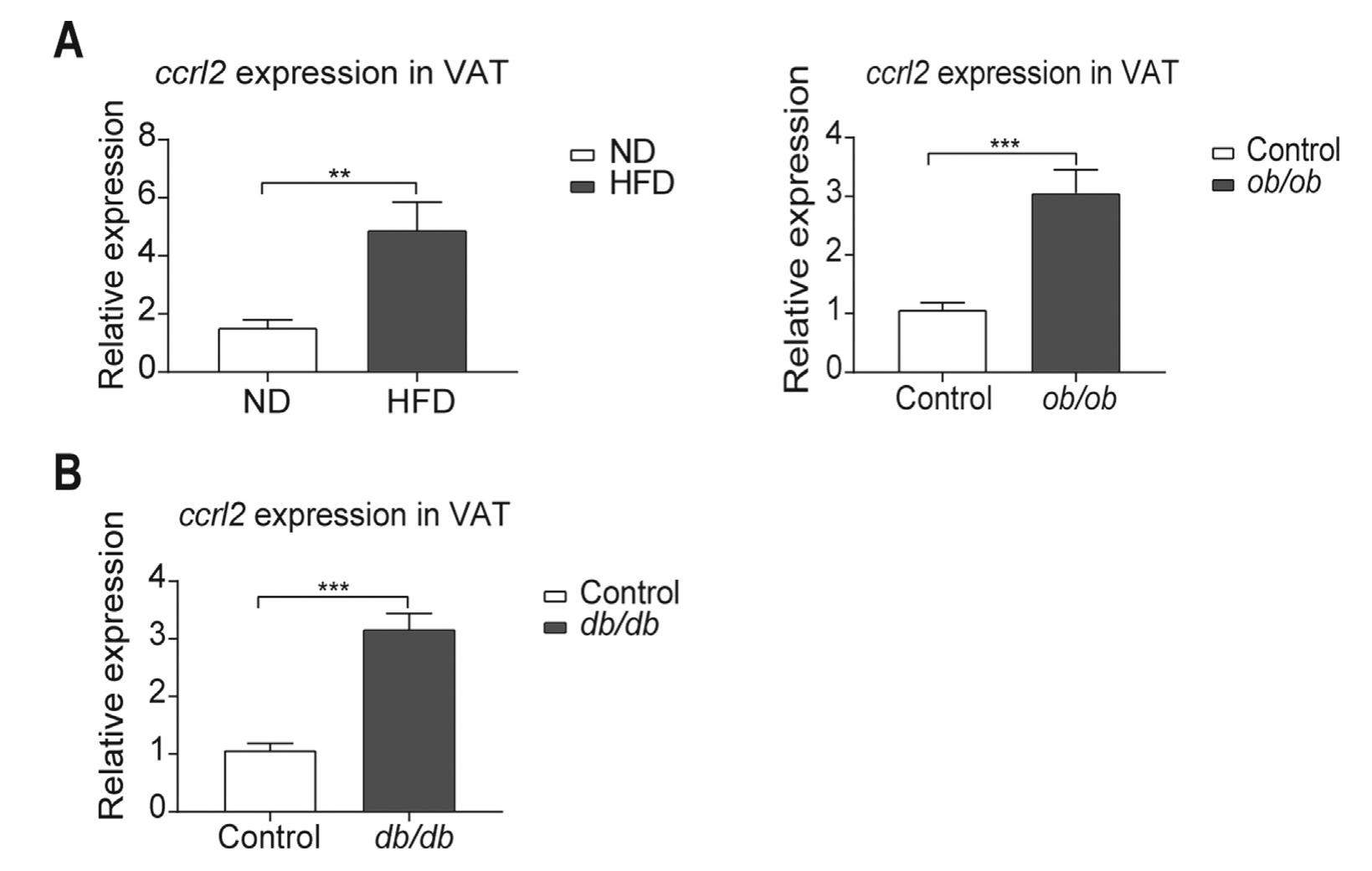
Obesity-induced inflammation, characterized by augmented infiltration and altered balance of macrophages, is a critical component of systemic insulin resistance. Chemokine-chemokine receptor system plays a vital role in the macrophages accumulation. CC-Chemokine Receptor-like 2 (Ccrl2) is one of the receptors of Chemerin, which is a member of atypical chemokine receptors (ACKR) family, reported taking part in host immune responses and inflammation-related conditions. In our study, we found ccrl2 expression significantly elevated in visceral adipose tissue (VAT) of high fat diet (HFD) induced obese mice and ob/ob mice. Systemic deletion of Ccrl2 gene aggravated HFD induced obesity and insulin resistance and ccrl2-/- mice showed aggravated VAT inflammation and increased M1/M2 macrophages ratio, which is due to the increase of macrophages chemotaxis in Ccrl2 deficiency mice. Cumulatively, these results indicate that Ccrl2 has a critical function in obesity and obesity-induced insulin resistance via mediating macrophages chemotaxis.