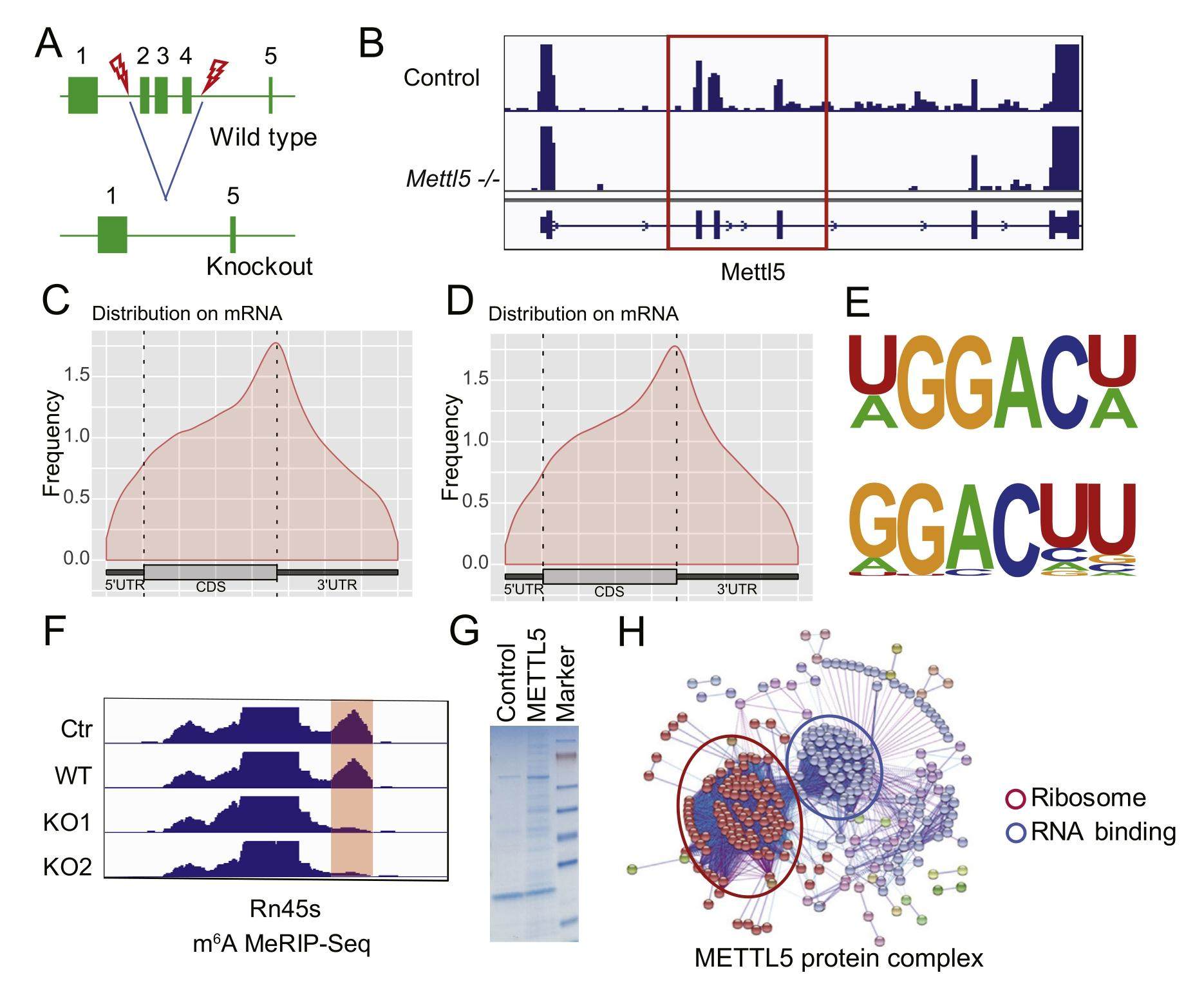
Mettl5 mediated 18S rRNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification controls stem cell fate determination and neural function


Ribosome RNA (rRNA) accounts for more than 80% of the cell's total RNA, while the physiological functions of rRNA modifications are poorly understood. Mutations of 18S rRNA m6A methyltransferase METTL5 cause intellectual disability, microcephaly, and facial dysmorphisms in patients, however, little is known about the underlying mechanisms. In this study, we identified METTL5 protein complex and revealed that METTL5 mainly interacts with RNA binding proteins and ribosome proteins. Functionally, we found that Mettl5 knockout in mESCs leads to the abnormal craniofacial and nervous development. Moreover, using Mettl5 knockout mouse model, we further demonstrated that Mettl5 knockout mice exhibit intellectual disability, recapitulating the human phenotype. Mechanistically, we found that Mettl5 maintains brain function and intelligence by regulating the myelination process. Our study uncovered the causal correlation between mis-regulated 18S rRNA m6A modification and neural function defects, supporting the important physiological functions of rRNA modifications in human diseases.