A critical role of the thioredoxin domain containing protein 5 (TXNDC5) in redox homeostasis and cancer development


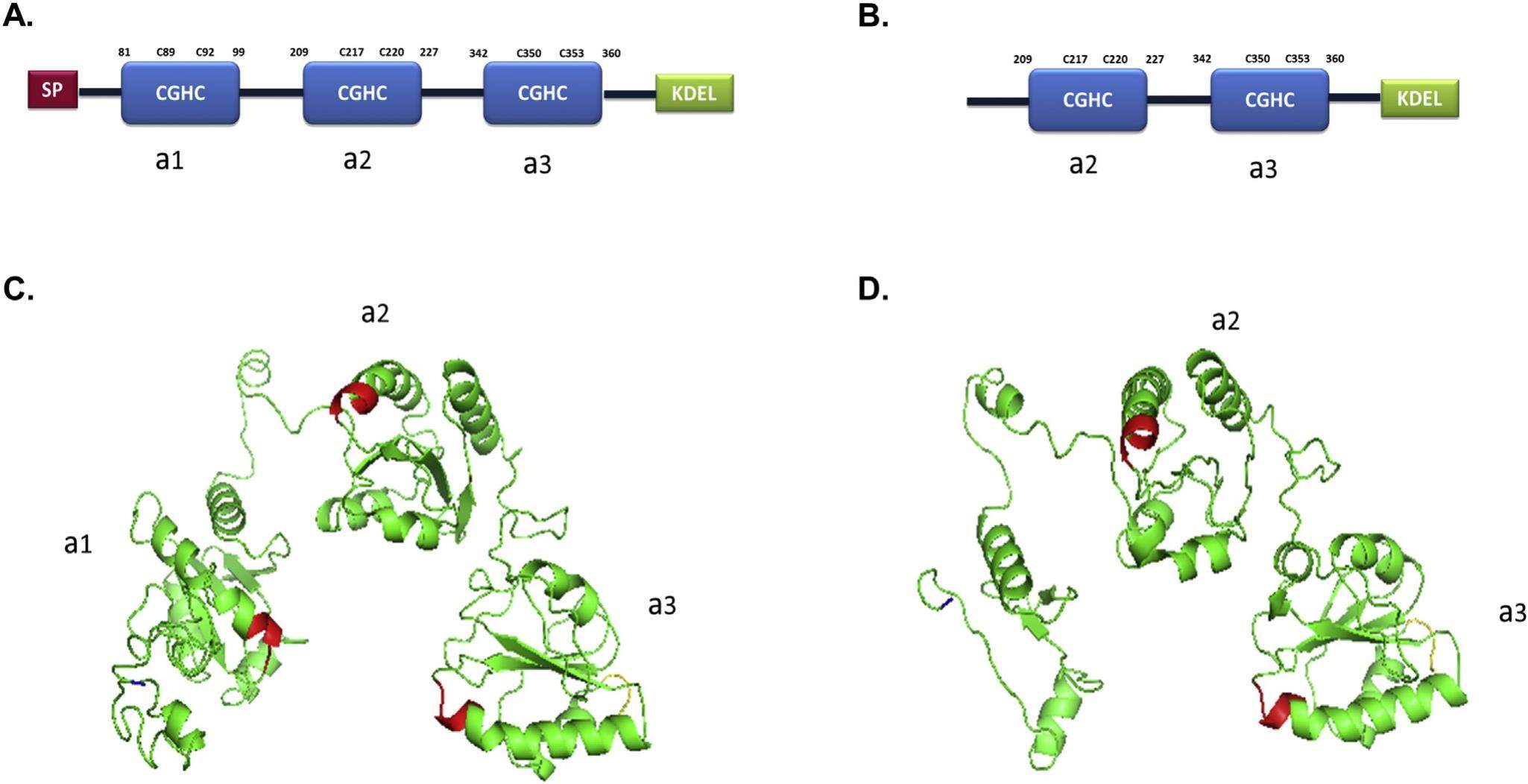
Correct folding of nascent peptides occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). It is a complicate process primarily accomplished by the coordination of multiple redox proteins including members of the protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) family. As a critical member of the PDI family, thioredoxin domain containing protein 5 (TXNDC5) assists the folding of newly synthesized peptides to their mature form through series of disulfide bond exchange reactions. Interestingly, TXNDC5 is frequently found overexpressed in specimens of many human diseases including various types of cancer. In this review, we summarized the biochemical function of TXNDC5 in mammalian cells and the recent progress on the understanding of its role and molecular mechanisms in cancer development. Findings of TXNDC5 in the activation of intracellular signaling pathways, stimulation of cell growth & proliferation, facilitation of cell survival and modulation of extracellular matrix to affect cancer cell invasion and metastasis are reviewed. These published studies suggest that strategies of targeting TXNDC5 can be developed as potentially valuable methods for the treatment of certain types of cancer in patients.