HOXB13 mutations and binding partners in prostate development and cancer: Function, clinical significance, and future directions


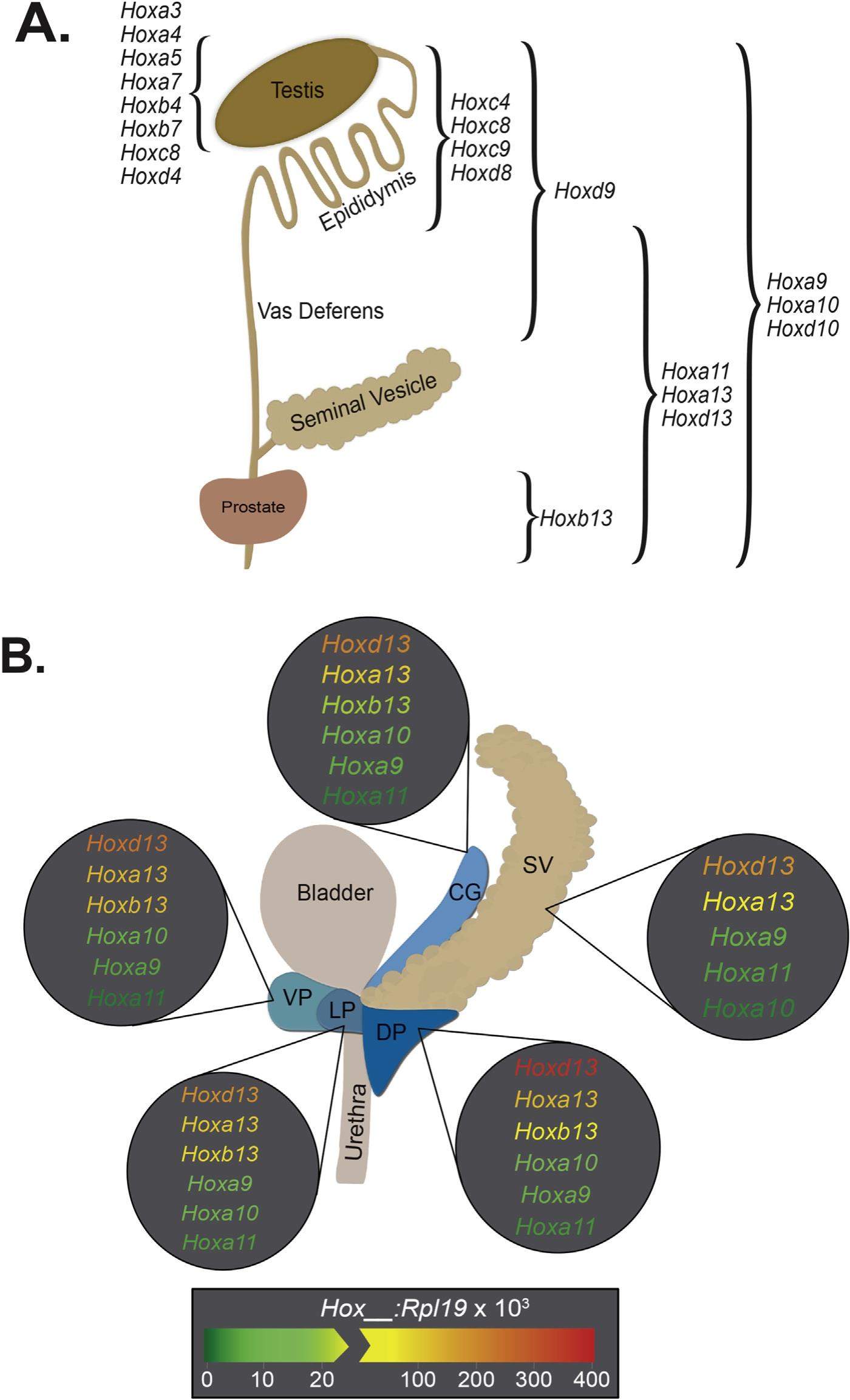
The recent and exciting discovery of germline HOXB13 mutations in familial prostate cancer has brought HOX signaling to the forefront of prostate cancer research. An enhanced understanding of HOX signaling, and the co-factors regulating HOX protein specificity and transcriptional regulation, has the high potential to elucidate novel approaches to prevent, diagnose, stage, and treat prostate cancer. Toward our understanding of HOX biology in prostate development and prostate cancer, basic research in developmental model systems as well as other tumor sites provides a mechanistic framework to inform future studies in prostate biology. Here we describe our current understanding of HOX signaling in genitourinary development and cancer, current clinical data of HOXB13 mutations in multiple cancers including prostate cancer, and the role of HOX protein co-factors in development and cancer. These data highlight numerous gaps in our understanding of HOX function in the prostate, and present numerous potentially impactful mechanistic and clinical opportunities for future investigation.