LncRNA KCNQ1OT1: Molecular mechanisms and pathogenic roles in human diseases


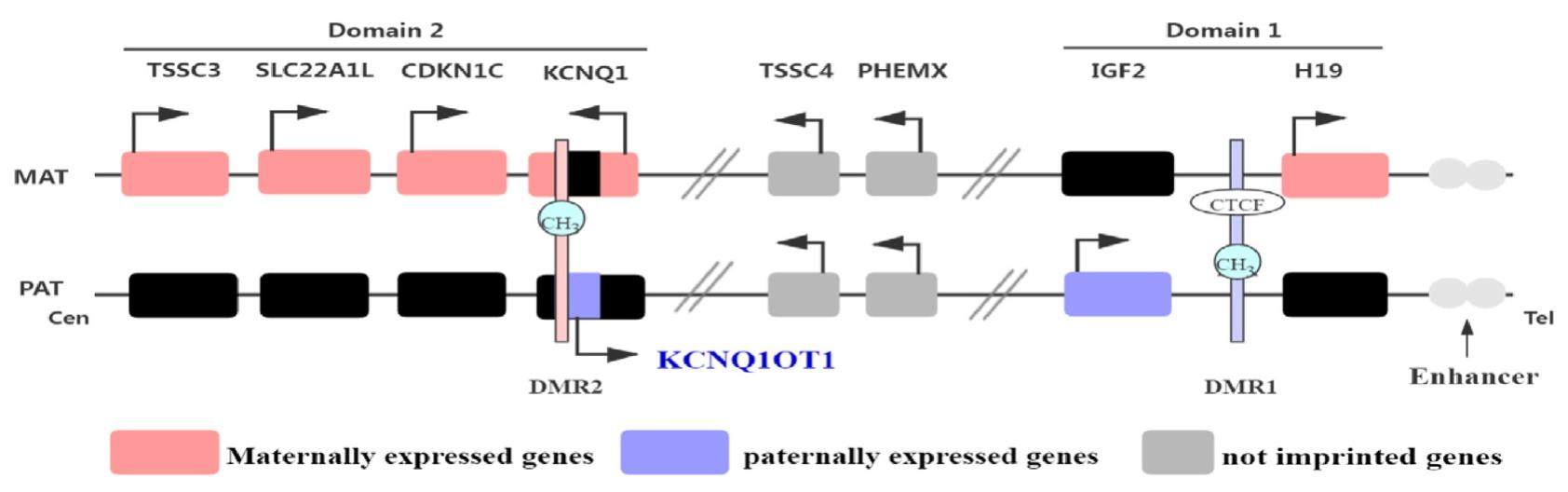
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) exhibit a length more than 200 nucleotides and they are characterized by non-coding RNAs (ncRNA) not encoded into proteins. Over the past few years, the role and development of lncRNAs have aroused the rising attention of researchers. To be specific, KCNQ1OT1, the KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1, is clearly classified as a regulatory ncRNA. KCNQ1OT1 is capable of interacting with miRNAs, RNAs and proteins, thereby affecting gene expression and various cell functions (e.g., cell proliferation, migration, epithelialemesenchymal transition (EMT), apoptosis, viability, autophagy and inflammation). KCNQ1OT1 is dysregulated in a wide range of human diseases (e.g., cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis and cataract), and it is speculated to act as a therapeutic target for treating various human diseases. On the whole, this review aims to explore the biological functions, underlying mechanisms and pathogenic roles of KCNQ1OT1 in human diseases.