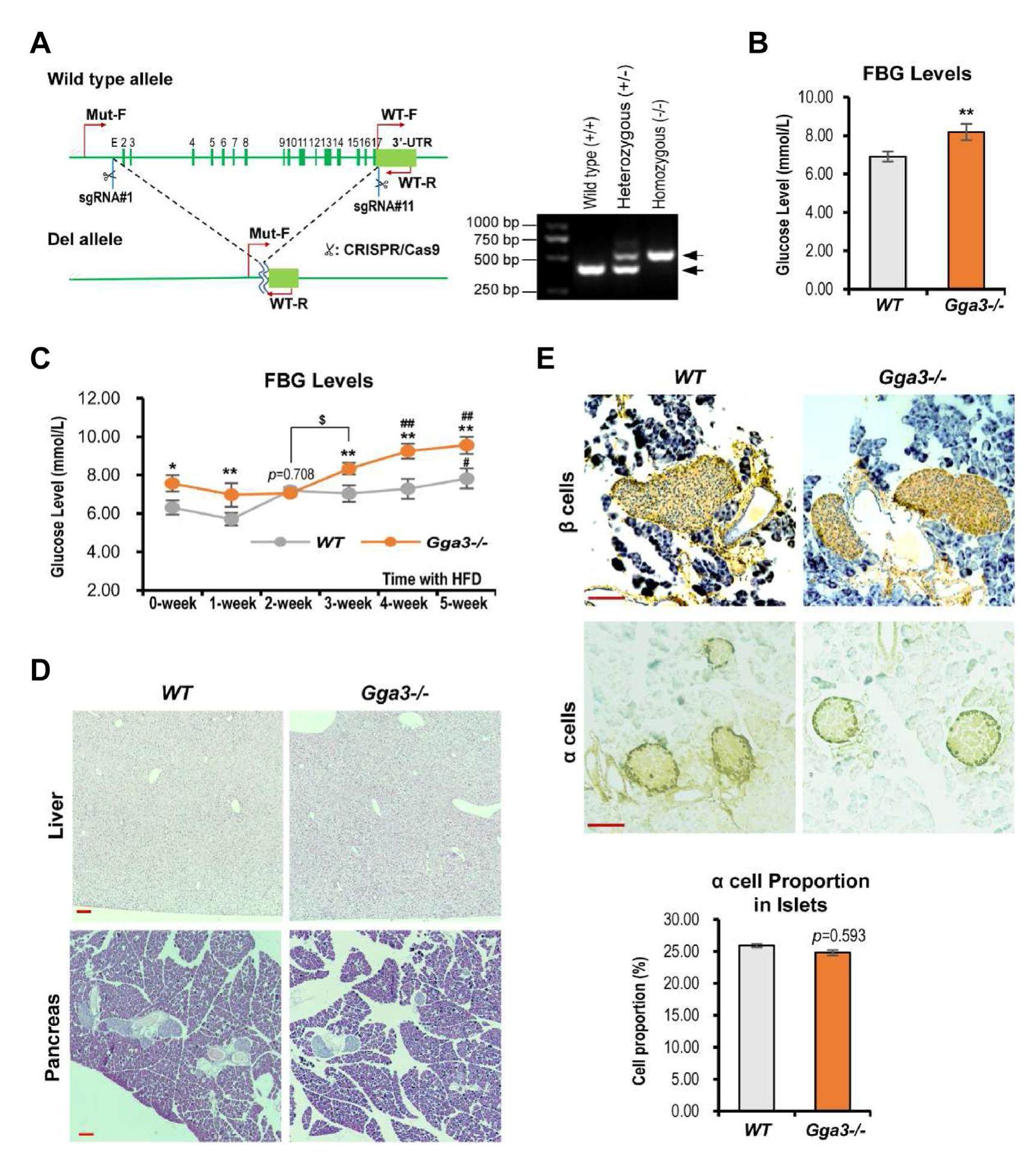
Gga3 gene-deleted C57BL/6J mice have elevated fasting blood glucose levels


Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the most common diseases in the elderly, and among DM patients, more than 90% have type 2 DM (T2DM). The etiology of T2DM is complex and associated with risk factors such as age, genetic disposition, and diet. The genetic factors underlying T2DM are currently the focus of intense research, and it has been established that the susceptibility genes associated with T2DM vary among different populations. A recent longitudinal exome-wide association study in the Japanese population has identified GGA3 as a susceptible locus for T2DM. GGA3 is one of the Golgi-localized g-ear-containing ARF binding proteins (GGAs) that function widely in the transport of Golgi-derived vesicles and in endocytic trafficking pathways. However, although it is widely acknowledged that the control of glucose homeostasis via endocytosis and glucose metabolism plays a vital role in T2DM, the associations between intracellular trafficking and diabetes pathogenesis have not been sufficiently established. In this study, we used a Gga3 gene knockout mouse strain to investigate the potential involvement of GGA3 in controlling blood glucose. The study was approved by the ethics committee of Jining Medical University (No. 2019-JS-005). Our results indicate that the GGA3 gene might play a protective role against diabetes.