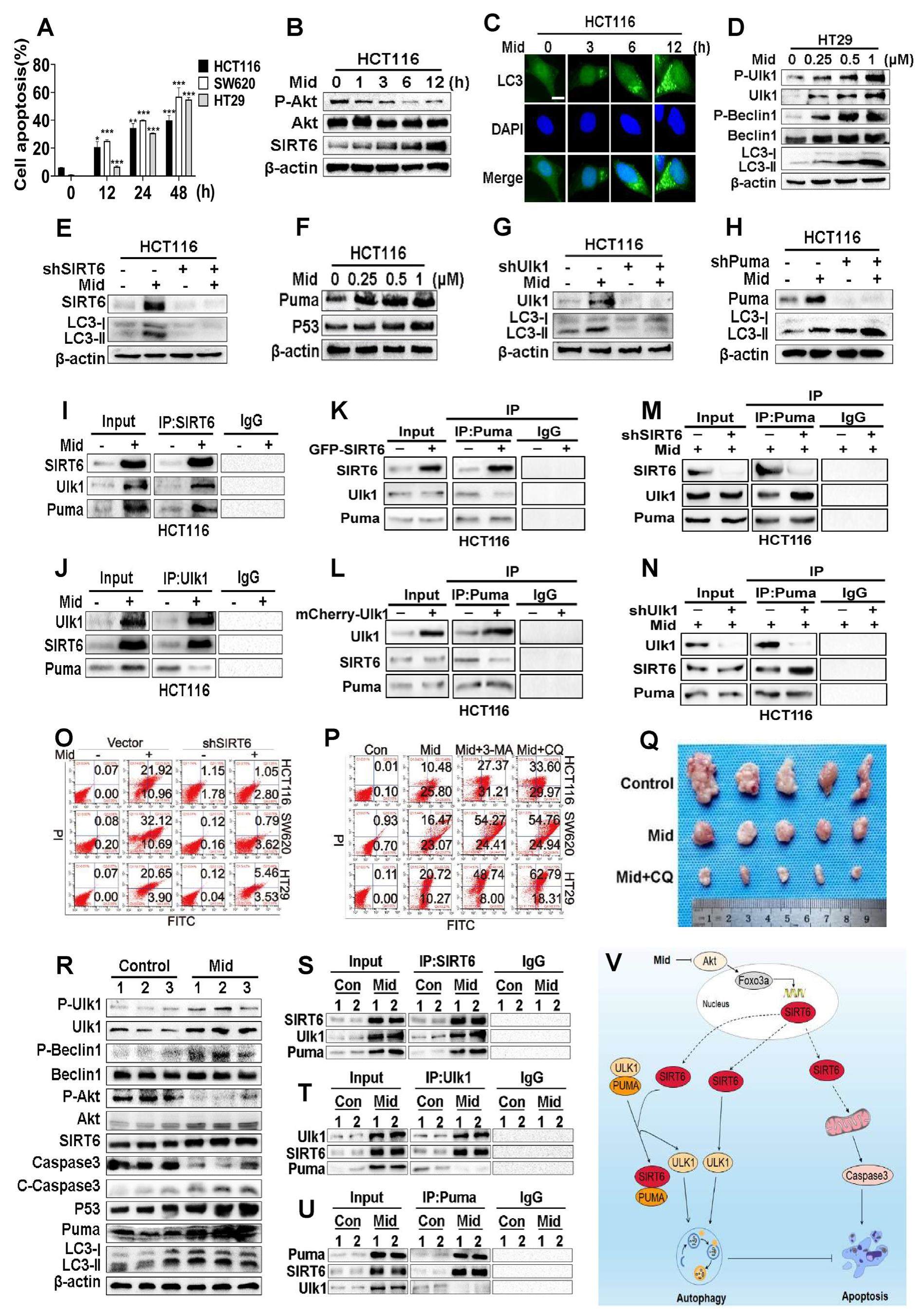
SIRT6 promotes autophagy through direct interaction with ULK1 and competitive binding to PUMA


Akt aberrant activation accelerated tumor development and metastasis, and our previous study identified silent information regulator 6 (SIRT6) as a novel and critical tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer (CRC) downstream of Akt. However, the function of SIRT6 in cancer progression has not been fully elucidated. In the present study, we found that except for inducing apoptosis, SIRT6 could serve as a crucial regulator to initiate autophagy by directlyinteractingwithandactivatingULK1. More importantly, we also reported autophagy regulation in a SIRT6-dependentindirectmanner, namely, SIRT6 competitively bound to PUMA, which led to the release of ULK1. Of note, autophagy inhibition enhanced the proapoptotic effect of Midostaurin both in vitro and in vivo. Summarily, SIRT6 induced apoptosis accompanied by protective autophagy, and SIRT6 promoted autophagy by directly interacting with ULK1 and competitive binding to PUMA. This new insight identified the dual function of SIRT6 on apoptosis and autophagy, which has attractive clinical applications in cancer therapy.