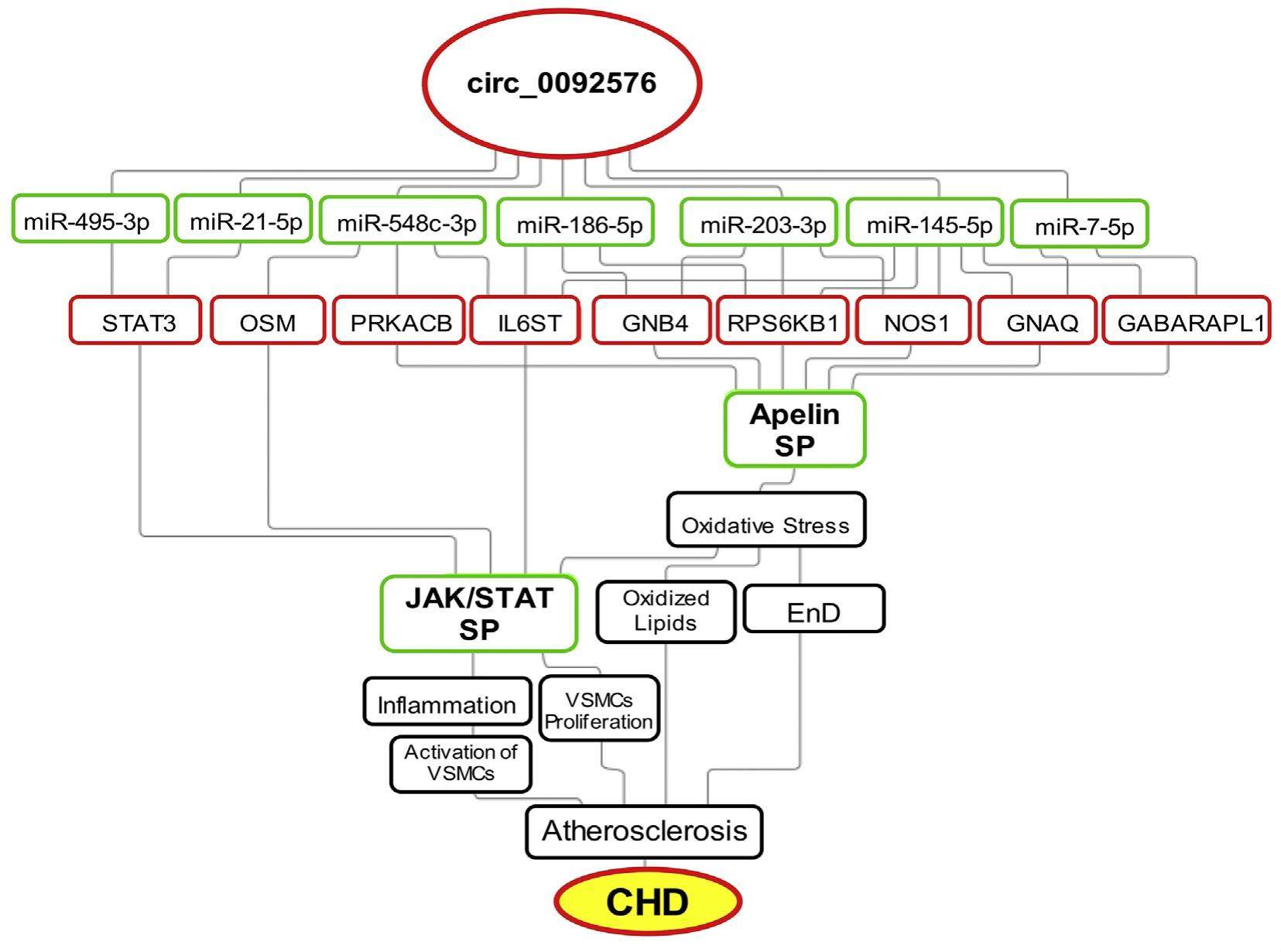
Identification of hsa_circ_0092576 regulatory network in the pathogenesis of coronary heart disease


Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are responsible for 30% of all deaths globally. Coronary heart disease (CHD), is the most common form of CVD, accounting for 46% of male and 38% female cardiovascular deaths. CHD is characterized by chronic inflammation and endothelial injuries in coronary arteries, and subsequent development of atherosclerotic plaques which eventually leads to myocardial ischemia. CHD is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors, and is prevalent in all parts of the world. Regulatory non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) e.g., long-chain ncRNAs, circRNAs, and miRNAs, are involved in the regulation of approximately 60% of protein-coding genes. Thus, ncRNAs partake in the regulation of many cellular processes. Dys-regulation of ncRNAs is a major underlying event in the pathogenesis of many diseases. Despite the vast information about CHD, frequency of the disease is still rising. Therefore, a study on the role of ncRNAs in CHD pathology is necessary to expand the understanding of molecular basis of the disease and pave way for its new diagnostic and treatment approaches. We demonstrated that hsa_-circ_0092576 and its target miRNAs are vital in the regulation of genes related to CHD pathology, and thus could be promising biomarkers of the disease.