Decreased expression of m6A demethylase ALKBH5 in decidua contributes to preeclampsia via m6A-CORIN-HuR pathway


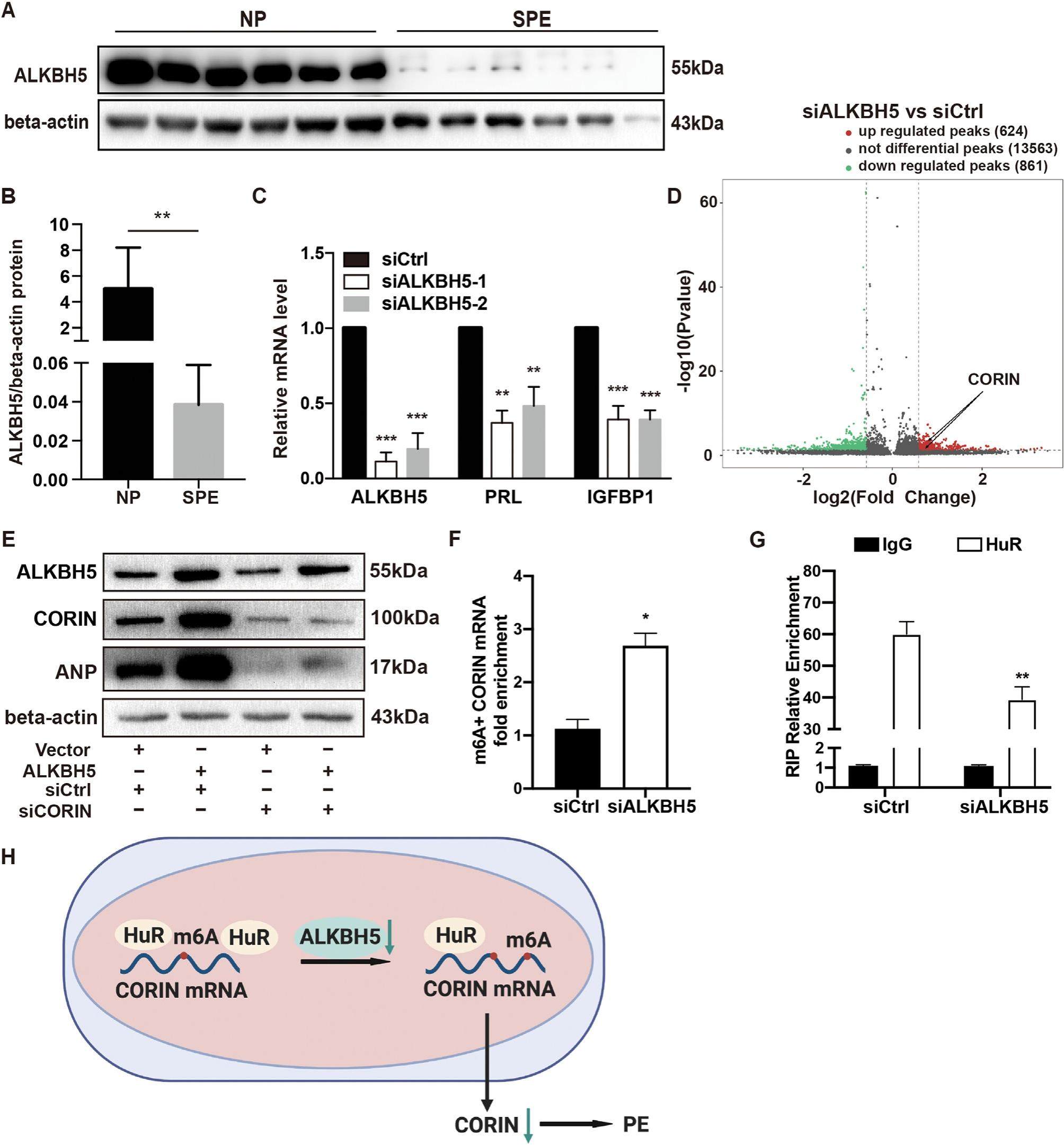
Preeclampsia (PE) is a pregnancy-specific hypertensive disorder which poses a severe threat to maternal and fetal health. Defective decidualization may contribute to PE. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is associated with various diseases. The regulatory mechanism of m6A in PE is not well established to date. We aimed to identify differentially expressed m6A and explore its regulatory role in the pathogenesis of PE. Here we showed that m6A demethylase alkB homolog 5 (ALKBH5) was lower expressed in the decidua of PE. Silencing ALKBH5 suppressed the decidualization of human endometrial stromal cells (hESCs) and the invasion of trophoblast (HTR-8) cells into hESCs. The meRIP-seq analysis revealed the altered expression of ALKBH5 target genes after ALKBH5 knocking down, including CORIN. CORIN is a cardiac protease that activates atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP). Mechanism study indicated that ALKBH5 demethylated CORIN transcripts, maintained CORIN stability and enhanced CORIN expression through HuR dependent pathway, which was essential for ALKBH5 to regulate the decidualization of hESCs and the invasion of HTR-8 cells. In conclusion, our data indicate that low ALKBH5 expression in PE decidua inhibits the decidualization of hESCs and trophoblast cell invasion through the regulation of CORIN and ANP via the m6A-HuR-dependent pathway.