Targeting CD47-SIRPα axis for Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma immunotherapy


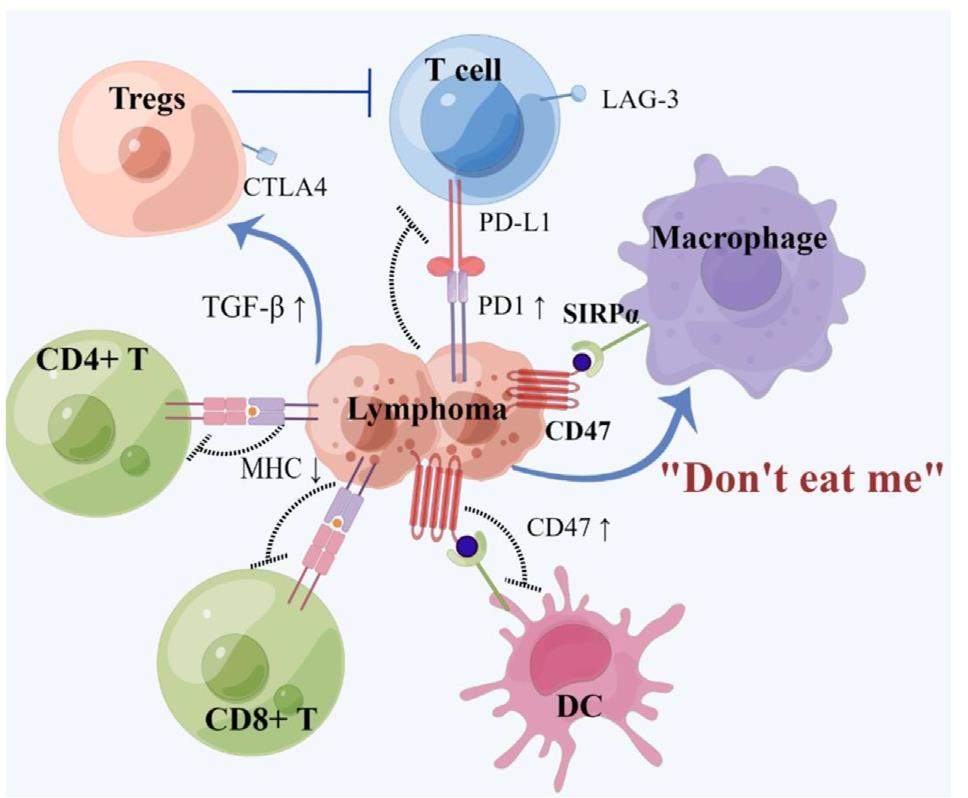
The interaction between cluster of differentiation 47 (CD47) and signal regulatory protein a (SIRPa) protects healthy cells from macrophage attack, which is crucial for maintaining immune homeostasis. Overexpression of CD47 occurs widely across various tumor cell types and transmits the "don’t eat me" signal to macrophages to avoid phagocytosis through binding to SIRPa. Blockade of the CD47-SIRPa axis is therefore a promising approach for cancer treatment. Lymphoma is the most common hematological malignancy and is an area of unmet clinical need. This review mainly described the current strategies targeting the CD47-SIRPα axis, including antibodies, SIRPa Fc fusion proteins, small molecule inhibitors, and peptides both in preclinical studies and clinical trials with Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.