ADAMTS2: More than a procollagen N-proteinase


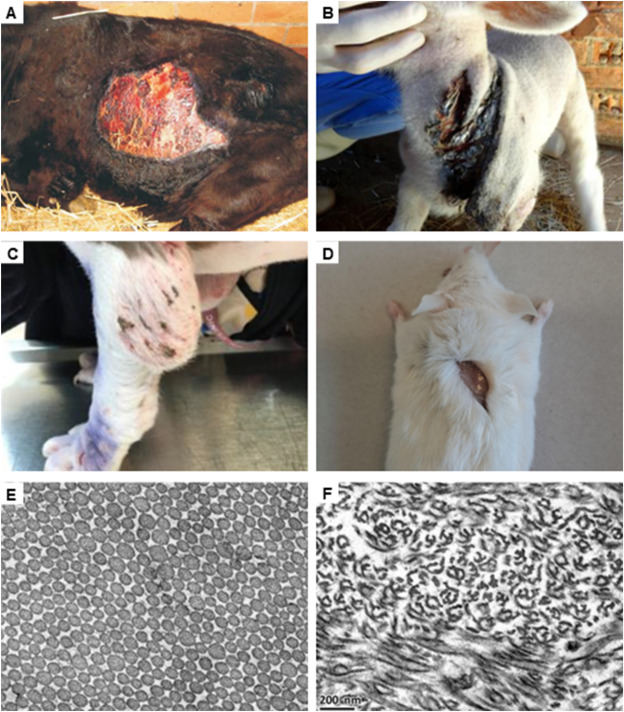
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 2 (ADAMTS2) is a member of the ADAMTS zinc metalloproteinase family, best known for its role as a procollagen I N-proteinase in the maturation of fibrillar collagens. Biallelic defects in the ADAMTS2 gene, resulting in a loss of ADAMTS2 enzyme activity and consequent retention of N-propeptides in type I procollagen molecules, lead to the rare monogenic disease Ehlers-Danlos syndrome dermatosparaxis type (dEDS) in humans, and dermatosparaxis in animals, conditions that are hallmarked by extreme fragility of the skin and other soft connective tissues. Recent studies have expanded the substrate repertoire of ADAMTS2 considerably, revealing its potential implication in several biological processes, including angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, neurodevelopment, immunity, and spermatogenesis. There is also emerging evidence for a role for ADAMTS2 in complex disorders, including cancer and cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disease. These findings may not only provide answers to hitherto unsolved questions in dermatosparaxis but also unveil a therapeutic and/or biomarker potential of ADAMTS2 in many diseases. This narrative review provides an in-depth overview of the discovery, structure, regulation, and enzymatic role of ADAMTS2, its role in fibrillar collagen maturation and in dEDS pathogenesis, as well as its newly discovered substrates and its potential role in complex disorders.