Single-cell sequencing reveals the expansion and diversity of T cell subsets in the bone marrow microenvironment of chronic myeloid leukemia


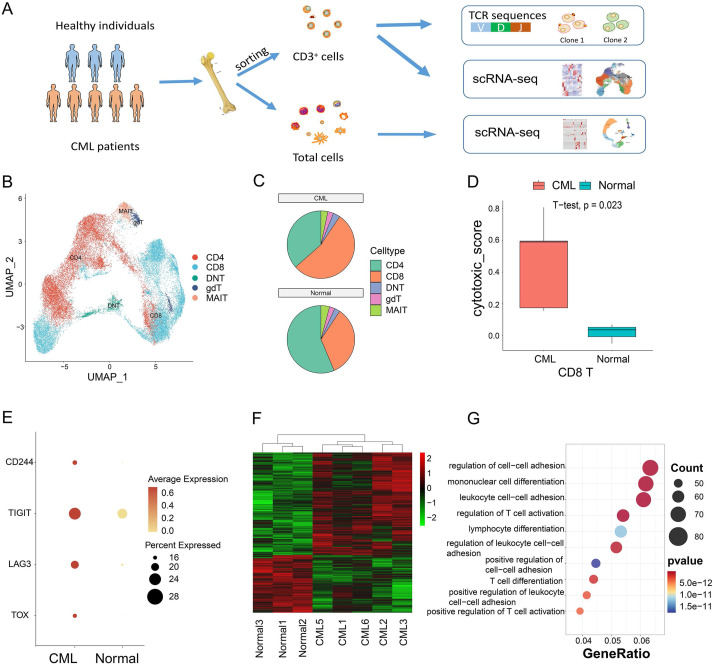
The immune microenvironment plays an important role in leukemia treatment. However, a specific single-cell profiling of the immune alteration in bone marrow of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients is still lacking. We performed multi-level single-cell sequencing to systematically decipher the bone marrow T cell atlas of CML patients. The results exhibited extensive changes of T cells, including the decreased CD4 T cells and increased CD8 T cells in the CML bone marrow. Subpopulation analysis revealed a significant increase of CD8 terminal effector (TE) cells and a significant decrease of CD4 naïve T cells. T cell receptor sequencing showed that the overall diversity of the T cell receptor repertoire was reduced in CML, with the exception of the CD8 TE cell. In addition, CD8 TE cells were the main source of gene expression differences in CD8 T cells. Intercellular communication analysis revealed the altered interaction between CD8 TE and other non-T cells in CML, including neutrophil subtype, indicating the potential regulation of bone marrow microenvironment cells on CD8 TE dynamics. Collectively, our work characterises the alteration of T cell subsets in CML patients at multiple single-cell levels, providing a valuable resource for understanding the immune microenvironment and developing new immune strategies for CML therapy.