Lactate transporter MCT4 regulates the hub genes for lipid metabolism and inflammation to attenuate intracellular lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease


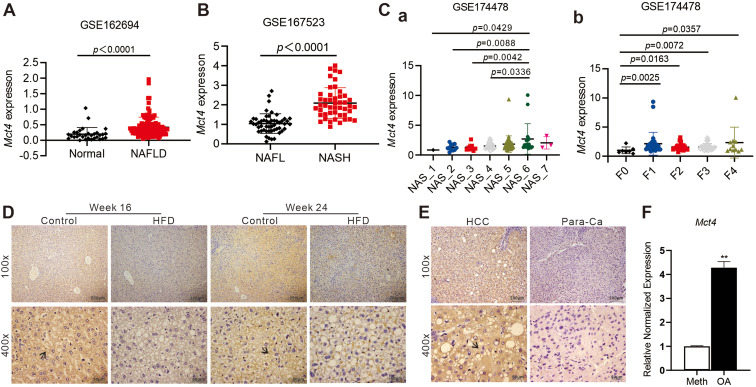
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients have multiple metabolic disturbances, with markedly elevated levels of lactate. Lactate accumulations play pleiotropic roles in disease progression through metabolic rearrangements and epigenetic modifications. Monocarboxylate transporter 4 (MCT4) is highly expressed in hepatocytes and responsible for transporting intracellular lactate out of the cell. To explore whether elevated MCT4 levels played any role in NAFLD development, we overexpressed and silenced MCT4 in hepatocytes and performed a comprehensive in vitro and in vivo analysis. Our results revealed that MCT4 overexpression down-regulated the genes for lipid synthesis while up-regulating the genes involved in lipid catabolism. Conversely, silencing MCT4 expression or inhibiting MCT4 expression led to the accumulation of intracellular lipid and glucose metabolites, resulting in hepatic steatosis. In a mouse model of NAFLD, we found that exogenous MCT4 overexpression significantly reduced lipid metabolism and alleviated hepatocellular steatosis. Mechanistically, MCT4 alleviated hepatic steatosis by regulating a group of hub genes such as Arg2, Olr1, Cd74, Mmp8, Irf7, Spp1, and Apoe, which in turn impacted multiple pathways involved in lipid metabolism and inflammatory response, such as PPAR, HIF-1, TNF, IL-17, PI3K-AKT, Wnt, and JAK-STAT. Collectively, our results strongly suggest that MCT4 may play an important role in regulating lipid metabolism and inflammation and thus serve as a potential therapeutic target for NAFLD.