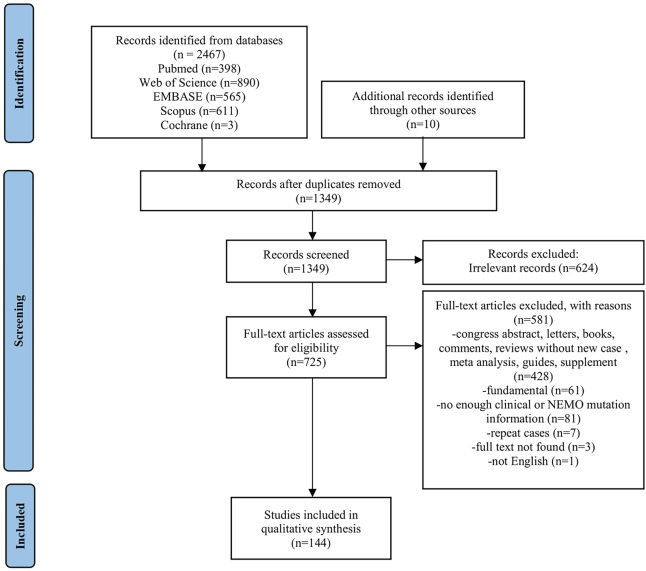
Clinical relevance of loss-of-function mutations of NEMO/IKBKG


Dysfunctional inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) kinase regulatory subunit gamma (IKBKG) is known to trigger incontinentia pigmenti (IP), anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia with immunodeficiency (EDA-ID), immunodeficiency (ID), and IKBKG deleted exon 5 autoinflammatory syndrome (NDAS). The correlation between genotype and phenotype remains elusive because of the considerable variability in IKBKG genes. This study aimed to systematically describe IKBKG gene mutations and clinical characteristics. Cases with IKBKG mutations and thorough clinical features were gathered using PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, Scopus, and Cochrane databases, with a publication deadline of February 12, 2023. The Newcastle-Ottawa scale and its modified version were used to assess the quality of each study. Gene mutations and clinical manifestation data were analyzed and reviewed. 144 publications with 564 patients were included in the analysis. IP, EDA-ID, ID, and NDAS accounted for 78.0%, 15.8%, 5.0%, and 1.2% of IKBKG mutations, respectively. Skin abnormalities (89.5%), dental abnormalities (68.5%), infection (100%), and non-infectious inflammation (100%) were the most common manifestations of IP, EDA-ID, ID, and NDAS, respectively. Mutations related to EDA-ID and ID are concentrated in the zinc finger region and characterized by the most severe clinical symptoms. E390RfsX5 can cause IP, EDA-ID, and ID. c.1182_1183delTT and H413R caused the most clinical manifestations. Mycobacterium (22.7%) and Streptococcus (17.5%) were the most common pathogens. Almost all cases of hyper-IgM occurred in patients with EDA-ID. Different structural domains correspond to symptoms with varying degrees of severity. Certain mutations may correspond to unique manifestations, providing insight into disease progression.