Identification of a splice site mutation in IL2RG in a Chinese boy with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency


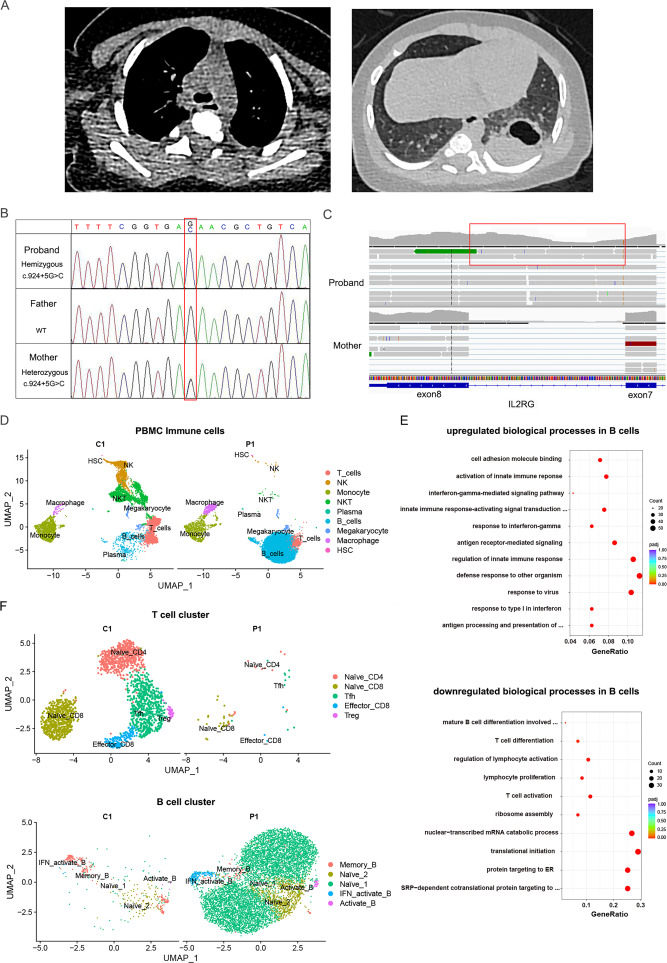
Interleukin 2 receptor gamma (IL2RG) is an important receptor component for interleukin-2 (IL2) family cytokines including IL2, IL4, IL7, IL9, IL15, and IL21.1 IL2RG is located on the X-chromosome q13.1, encoding a common gamma chain (γC) that is essential in lymphoid development, especially in the modulation of T cell and natural killer (NK) cell immune responses. Mutations in the IL2RG gene cause X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (X-SCID), which is a life-threatening rare disease. In typical X-SCID, the disease is characterized by a nearly complete absence of T cells and NK cells, alongside normal or elevated counts of non-functional B cells (T– B+ NK− phenotype). Infants with X-SCID exhibit high susceptibility to bacterial and opportunistic infections. Here, we report a splice site mutation (c.924+5G > C) in the IL2RG gene in a 3-month-old boy presenting with a typical phenotype of X-SCID.