Bcl6 controls the stability and suppressive function of regulatory T cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma


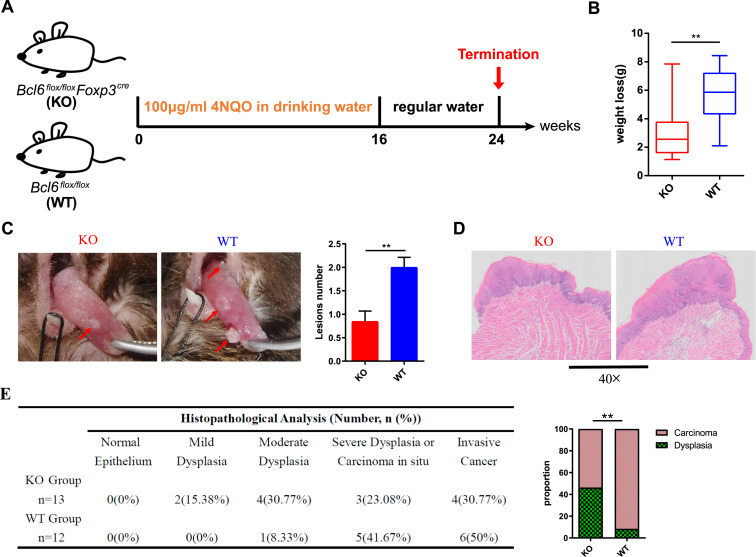
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) ranks as the sixth most common cancer globally. Most studies in HNSCC demonstrated that regulatory T (Treg) cells confine the anti-tumor activity of effector T cells which may contribute to the immune escape and uncontrolled tumor progression. Here, we uncovered that the specific abrogation of Bcl6 in Treg cells resulted in significantly delayed malignant transformation of 4NQO-induced tumorigenesis. Bcl6 deficiency impairs the lineage stability of Treg cells by down-regulating the histone H3K4 trimethylation. Importantly, Bcl6 inhibition repressed the tumor growth of murine HNSCC and exhibited synergistic effects with immune checkpoint blockade therapy. These findings suggest that Bcl6 can be exploited as a promising therapeutic target for HNSCC treatment.