Emerging roles for fatty acid oxidation in cancer


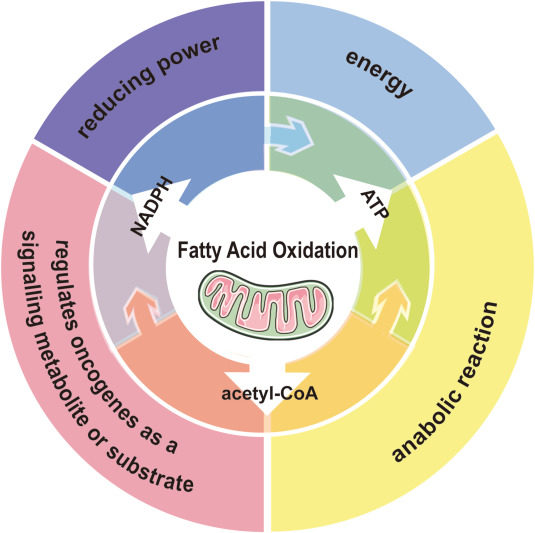
Fatty acid oxidation (FAO) denotes the mitochondrial aerobic process responsible for breaking down fatty acids (FAs) into acetyl-CoA units. This process holds a central position in the cancer metabolic landscape, with certain tumor cells relying primarily on FAO for energy production. Over the past decade, mounting evidence has underscored the critical role of FAO in various cellular processes such as cell growth, epigenetic modifications, tissue-immune homeostasis, cell signal transduction, and more. FAO is tightly regulated by multiple evolutionarily conserved mechanisms, and any dysregulation can predispose to cancer development. In this view, we summarize recent findings to provide an updated understanding of the multifaceted roles of FAO in tumor development, metastasis, and the response to cancer therapy. Additionally, we explore the regulatory mechanisms of FAO, laying the groundwork for potential therapeutic interventions targeting FAO in cancers within the metabolic landscape.