Characterization of a novel HIV-1 second-generation circulating recombinant form (CRF144_07C) in Ganzhou, China


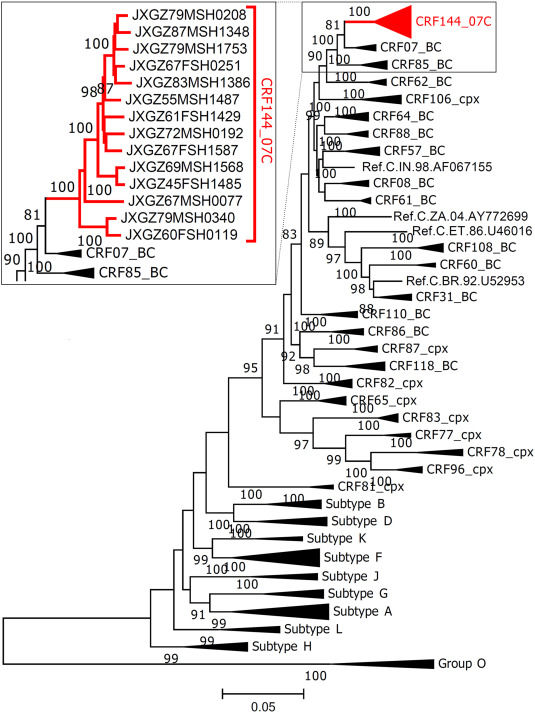
Inter-subtype recombination is the main force for the complexity of HIV-1 genetic diversity, which increases the difficulty of preventing HIV-1 infection and administering antiretroviral therapy for people living with HIV. To date, 143 circulating recombinant forms (CRFs) have been reported globally, 43 of which were identified in China.1 Moreover, HIV-1 strains that are produced by second-generation combinations, including unique recombinant forms and CRFs, such as CRF105_0108, CRF123_0107, and CRF134_0185, have been commonly reported in recent years. The present study identified a novel second-generation recombinant form of HIV-1 comprising CRF07_BC and subtype C and designated CRF144_07C. To our knowledge, this was the first report of HIV CRFs comprising CRF07_BC and subtype C, further indicating the complexity of HIV genetic diversity in China.