Molecular mechanism of tumor-infiltrating immune cells regulating endometrial carcinoma


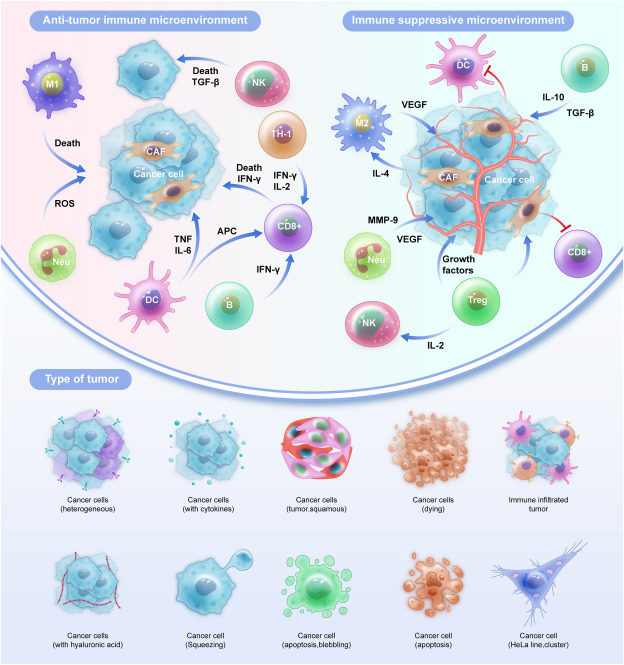
Endometrial carcinoma (EC) is a prevalent gynecological cancer, and its interaction with the immune system is pivotal in cancer progression. This comprehensive review explores the molecular mechanisms involved in the regulation of EC by tumor-infiltrating immune cells. This review discusses the composition and functions of various immune cell types within the tumor microenvironment, including T cells, B cells, macrophages, and natural killer cells, and elucidates their specific roles in cancer control. It also delves into the immune evasion strategies employed by EC cells, with a specific focus on immune checkpoint pathways and their influence on tumor development. Signaling pathways, cytokines, and chemokines mediating immune responses within the tumor microenvironment are also detailed. Furthermore, clinical implications and therapeutic strategies, such as immunotherapies, are also reviewed, and relevant clinical trials are discussed. Additionally, this review discusses the existing gaps in our knowledge, suggests potential avenues for future research, and emphasizes the significance of understanding these mechanisms for enhanced EC treatment. This review provides an exhaustive overview of the current knowledge, supporting the ongoing quest for more effective therapeutic interventions on EC.