AUTS2 expression within mammalian lineage: A predictor of neural networks involved in autism spectrum disorders


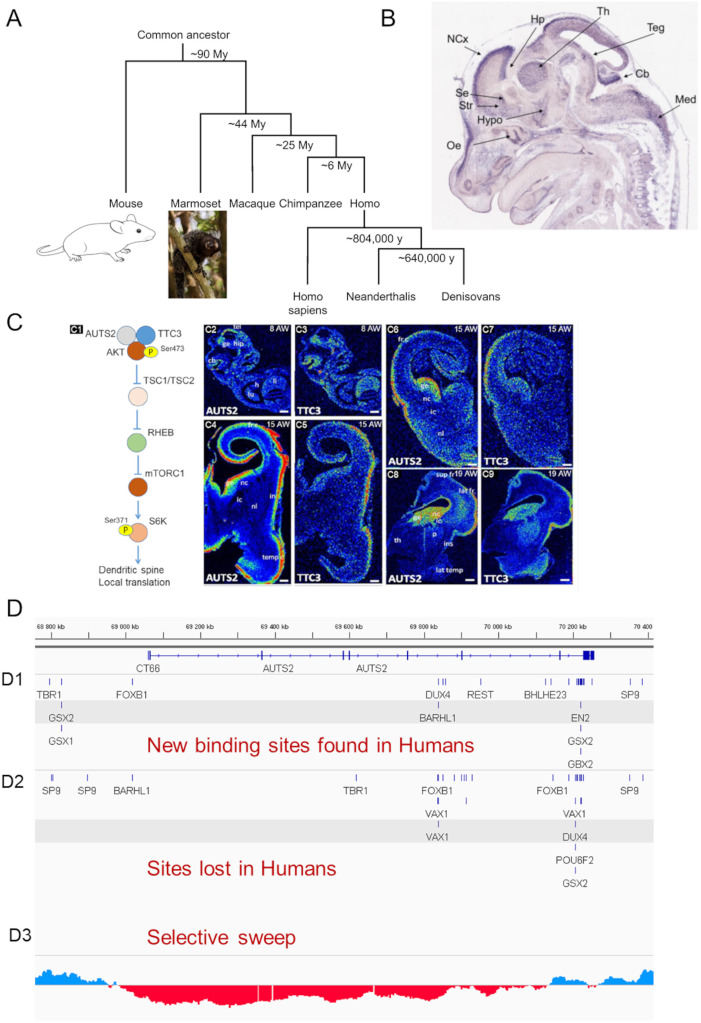
The autism susceptibility candidate 2 (AUTS2) gene1,2 at 7q11.2 was first identified and found disrupted because of a balanced translocation in a pair of monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Analysis of 60 novel cases suggests that clinical phenotypes are more closely associated with intellectual disability rather than directly linked to ASD features. Human AUTS2 is a highly conserved gene that spans 1.2 Mb. Human AUTS2 protein has two major isoforms, full-length (1259 aa) and C-terminal (711 aa). Phenotypic analysis of patients indicated that they had borderline to severe intellectual disability/developmental delay, and 83%–100% had microcephaly. Mild dysmorphology was present. Specific traits of autism (like obsessive behavior) were seen frequently (83%). AUTS2 is also associated with alcohol consumption, heroin dependence, schizophrenia, and dyslexia, as analyzed using GWAS studies.