Utilization of cuproptosis-related lncRNAs to predict the prognosis of pancreatic cancer patients and explore their roles in immune cell infiltration and prognosis evaluation


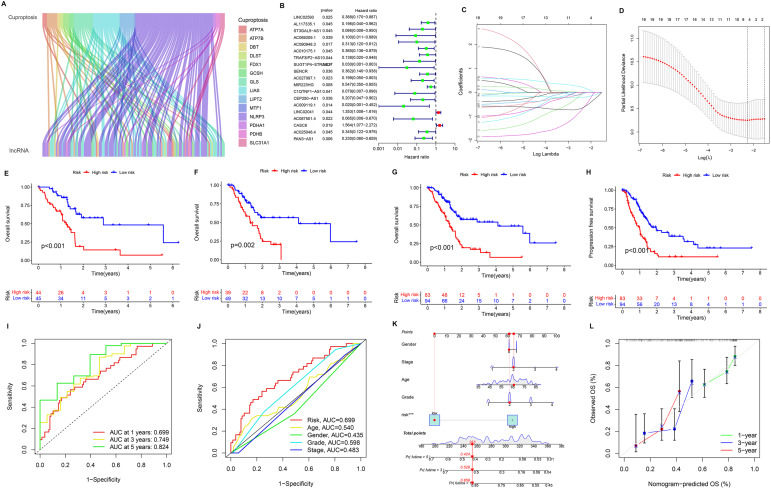
The prognosis of pancreatic cancer (PC) is difficult to predict1 and is extremely poor.2 Studies showed that cuproptosis was related to PC. The roles are not completely understood. It is considered that lncRNAs are closely associated with PC. We explored the relationship of curproptosis-related lncRNAs (CRLs) with the prognosis of PC patients and their potential role. We determined 19 prognostic CRLs through Pearson correlation analysis and univariate Cox regression analysis from 185 tumor samples. Subsequently, we constructed a predictive prognosis model for PC patients based on four CRLs and utilized the formula to calculate the risk score. The values for the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) were 0.699, 0.749, and 0.824 at 1 year, 3 years, and 5 years, respectively, which suggested that our risk model showed good predictive ability. Besides, we found the potential regulatory pathways by enrichment analysis, obtained the differences in immune microenvironment and drug sensitivity in different risk groups, and found that drug sensitivity in the high-risk group of other drugs was significantly lower. The prognostic model can accurately evaluate the prognosis for PC patients. These CRLs were related to the immune microenvironment, which can become underlying biomarkers for PC prediction, immunotherapy, and drug therapy.