HER3: Unmasking a twist in the tale of a previously unsuccessful therapeutic pursuit targeting a key cancer survival pathway


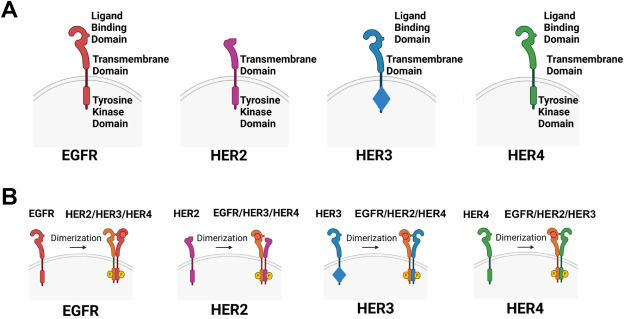
HER3, formally referred to as ERB-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 3, is a member of the ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases (also known as EGFR) family. HER3 plays a significant pro-cancer role in various types of cancer due to its overexpression and abnormal activation, which initiates downstream signaling pathways crucial in cancer cell survival and progression. As a result, numerous monoclonal antibodies have been developed to block HER3 activation and subsequent signaling pathways. While pre-clinical investigations have effectively showcased significant anti-cancer effects of HER3-targeted therapies, these therapies have had little impact on cancer patient outcomes in the clinic, except for patients with rare NRG1 fusion mutations. This review offers a comprehensive description of the oncogenic functions of HER3, encompassing its structure and mediating signaling pathways. More importantly, it provides an in-depth exploration of past and ongoing clinical trials investigating HER3-targeted therapies for distinct types of cancer and discusses the tumor microenvironment and other critical determinants that may contribute to the observed suboptimal outcomes in most clinical studies using HER3-targeted therapies. Lastly, we suggest alternative approaches and the exploration of novel strategies to potentially improve the efficacy of targeting the pivotal oncogenic HER3 signaling pathway in future translational investigations.