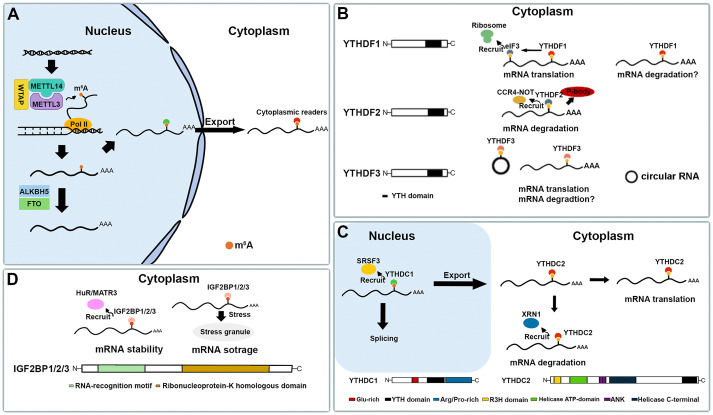
The regulatory role of m6A modification in the maintenance and differentiation of embryonic stem cells


As the most prevalent and reversible internal epigenetic modification in eukaryotic mRNAs, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) post-transcriptionally regulates the processing and metabolism of mRNAs involved in diverse biological processes. m6A modification is regulated by m6A writers, erasers, and readers. Emerging evidence suggests that m6A modification plays essential roles in modulating the cell-fate transition of embryonic stem cells. Mechanistic investigation of embryonic stem cell maintenance and differentiation is critical for understanding early embryonic development, which is also the premise for the application of embryonic stem cells in regenerative medicine. This review highlights the current knowledge of m6A modification and its essential regulatory contribution to the cell fate transition of mouse and human embryonic stem cells.