Integrated analyses reveal the prognostic and immunotherapeutic value of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related genes in cancer


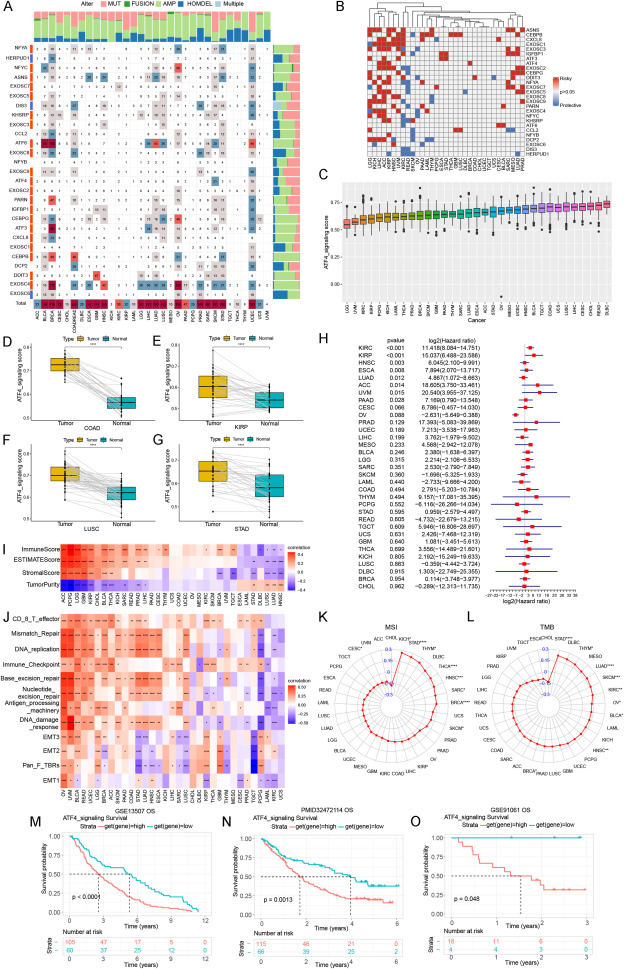
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is a procedure that results from increased protein release or improper ER protein folding, which is emerging as a possible driver of pathological conditions such as cancer, cardiometabolic diseases, rheumatic disease, and neurodegenerative diseases.1,2 Activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4), which is considered the primary controller of the cellular reaction when subjected to external stress,3 plays a vital role in amino acid metabolism, differentiation, metastasis, angiogenesis, and stress-related oxidative resistance.4 However, the prognosis value and immune signature of ATF4 activating genes in tumors are still unclear. Therefore, a better understanding of the role of ATF4 activating genes will promote new approaches to tumor treatment. In this work, we set up a model based on the expression level of ATF4 signaling-related genes, and ATF4 signaling score, which reflects the level of ER stress. Then we explored the expression profile of genes relevant to ATF4 signaling and evaluated the association between ATF4 signaling score and the prognosis of cancer patients. Additionally, our study explored the connection between ATF4 signaling score and tumor immunologic characteristics. Therefore, the current work provides a thorough analysis of the expression of 27 ATF4 signaling-related genes in 33 different kinds of cancers. Our results further demonstrate the potential of ATF4 signaling in tumor development and immunotherapy.