The silencing transcription factor REST targets UCHL1 to regulate inflammatory response and fibrosis during cardiac hypertrophy


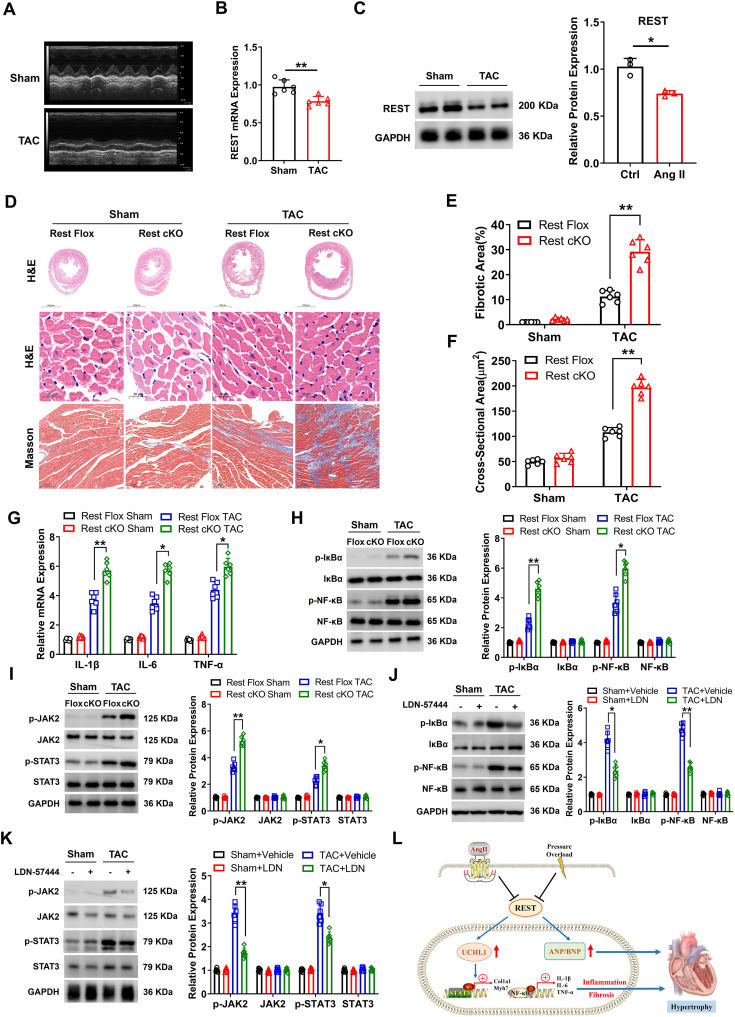
RE1 silencing transcription factor (REST) plays a key role in embryonic development and fetal cardiac gene reactivation.1 However, understanding of the role of REST in cardiac remodeling is very limited. A recent study has shown that cardiac-specific REST knockout increases Gαo expression, and impairs Ca2+ processing in ventricular myocytes, leading to cardiac dysfunction.2 Moreover, REST could bind to the neuron-restrictive silencer element region of the UCHL1 (ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1) gene promoter and regulate the expression of UCHL1.3 A recent study has reported that UCHL1 is significantly up-regulated in hypertrophic hearts, and positively regulates cardiac hypertrophy through stabilizing epidermal growth factor receptors.4 Here, we found that cardiac-specific REST knockout (REST cKO) mice showed more severe fibrosis and inflammation following pressure overload conditions. REST deficiency up-regulated UCHL1 expression, which then exacerbated cardiac hypertrophy. Whatmore, the application of UCHL1 inhibitor LDN-57444 in the REST cKO mice could alleviate fibrosis and inflammation in hypertrophic hearts via the NF-κB (nuclear factor-κB) and STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) signaling pathways.