Unique anti-angiogenic effects, pharmacological targets and therapeutic mechanisms of Chinese herbal medicines for endometriosis


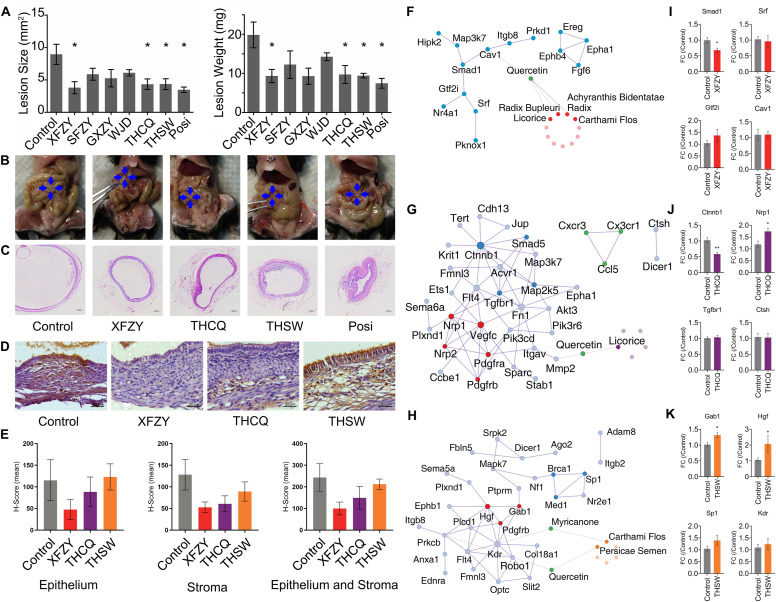
Endometriosis is a common and benign angiogenesis-dependent gynecological disorder, which refers to the proliferation and growth of endometrium-like tissues with neovasculature formation outside of the uterus.1 Available medical treatments for endometriosis containing hormonal and non-hormonal treatments had been limited for long-term usage by their side effects.2 Ideal medical treatment for endometriosis with efficacy to relieve symptoms and suppress endometriotic lesion growth and minimal side effects has been longing for decades.3 Angiogenesis is a promising therapeutic target for endometriosis.4 Chinese herbal medicines (CHM), as a mainstream medication in China and many other Asian countries, have been commonly used for women with endometriosis.5 However, there is no scientific evaluation of their anti-endometriosis and anti-angiogenic effects on endometriosis. Clinical trials can only include limited interventions for comparison and a large sample size is required to achieve statistical power for outcome measures of interest. Herewith, an experimental endometriosis mouse model was applied to investigate and compare the anti-angiogenic effect, targets, and mechanism of CHM. In this study, anti-angiogenic effects, pharmacological targets, and therapeutic mechanisms of commonly used CHM formulae, including Shaofu Zhuyu Tang (SFZY), Xuefu Zhuyu Tang (XFZY), Gexia Zhuyu Tang (GXZY), Wenjing Tang (WJD), Taohe Chengqi Tang (THCQ), and Taohong Siwu Tang (THSW) in the mouse model were studied (Table S1).