Prognosis prediction and immune microenvironment features of breast cancer indicated by a cuproptosis-associated long non-coding RNA signature


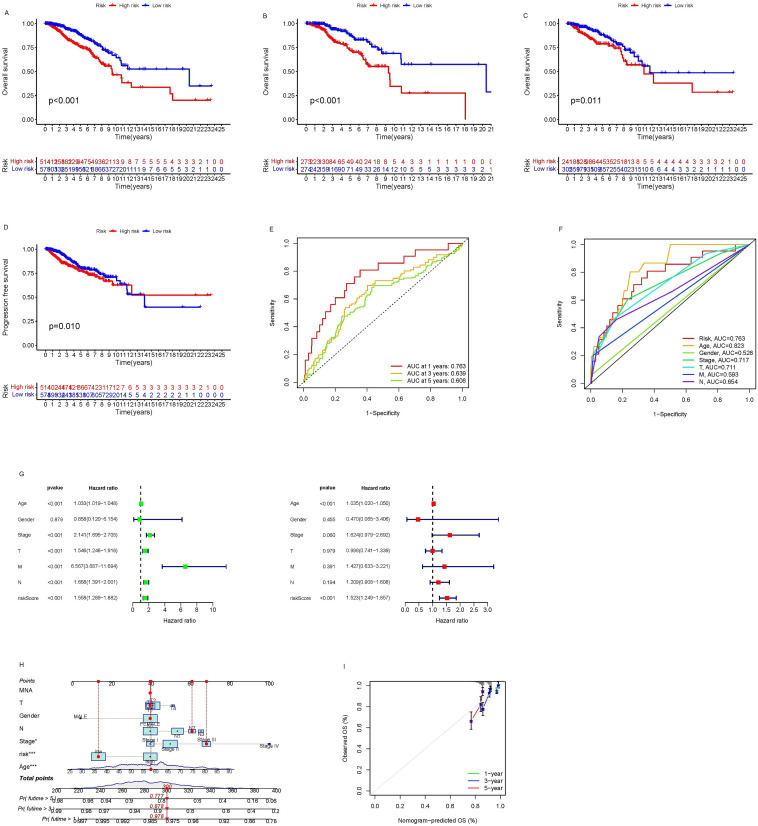
Cuproptosis is a newly discovered type of programmed cell death that involves the depletion of intracellular copper and is not influenced by other inhibitors of programmed cell death. This modality was first identified and named by Tsvetkov et al in the previous year.1 To further explore the relationship between cuproptosis, the tumor microenvironment, immunotherapy, and prognosis for breast cancer (BC), the expression patterns of 19 cuproptosis-related long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) were determined using data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Through Cox and Lasso regression analyses, we identified three crucial lncRNAs: AL137847.1, LRRC8C-DT, and NIFK-AS1. These lncRNAs were selected to establish a risk prediction model. Additionally, a nomogram was constructed by combining the clinical characteristics with the developed model. Differential expression analysis and functional enrichment analysis were performed based on the high- and low-risk groups derived from the risk prediction model. In addition, the mutant landscape of lncRNAs in the TCGA cohort was investigated, and the correlation between tumor mutational burden (TMB), immune activation pathways, and the prognostic model was analyzed. Real-time quantitative PCR experiments confirmed that the expression levels of AL137847.1, LRRC8C-DT, and NIFK-AS1 were significantly higher in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells compared with normal mammary epithelial cells. Furthermore, drug sensitivity analyses were carried out. The findings of this study may serve as a reference for individualized prognosis prediction and immunotherapy strategies for BC patients.