Integrative analysis of tumor stemness and immune microenvironment deciphers novel molecular subtypes in hepatocellular carcinoma


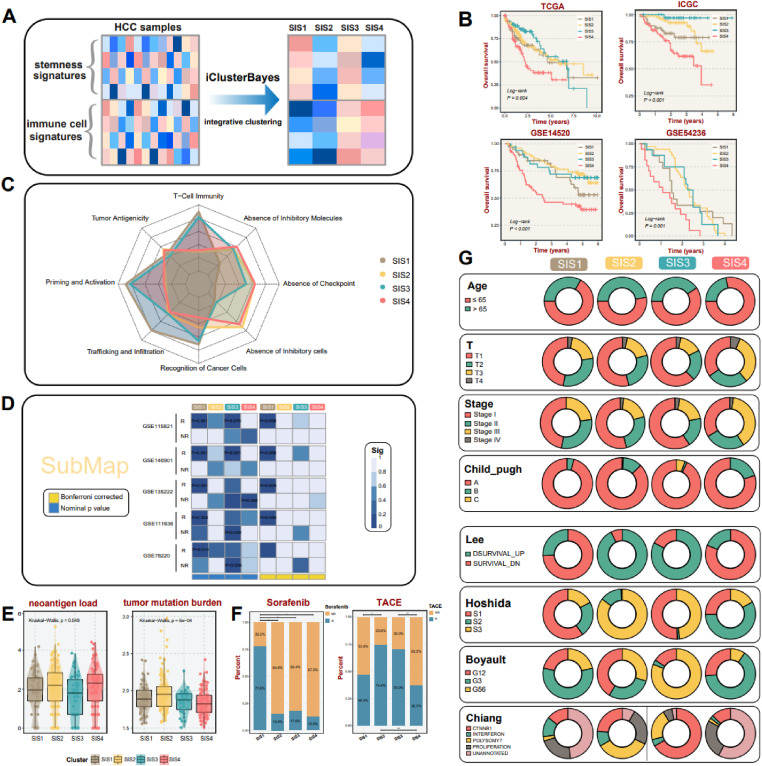
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a highly heterogeneous tumor, with dynamic equilibrium and complex interplay between its intricate tumor nature and ambient tumor immune microenvironment (TIME).1 Elegant research has indicated that cancer stem cells, a small subset of neoplastic cells confined within dedicated niches, display stem cell-like properties and interact with cells in TIME, thereby imparting an indelible impact on stemness regulation, tumor heterogeneity, and cancer cell plasticity.2 Previous taxonomies solely from the perspective of stemness or TIME may introduce some degree of bias in the comprehension of HCC carcinogenesis,3,4 and thus it is of paramount importance to systematically consider tumor stemness and TIME as a whole to truly portray the biological landscape of HCC.