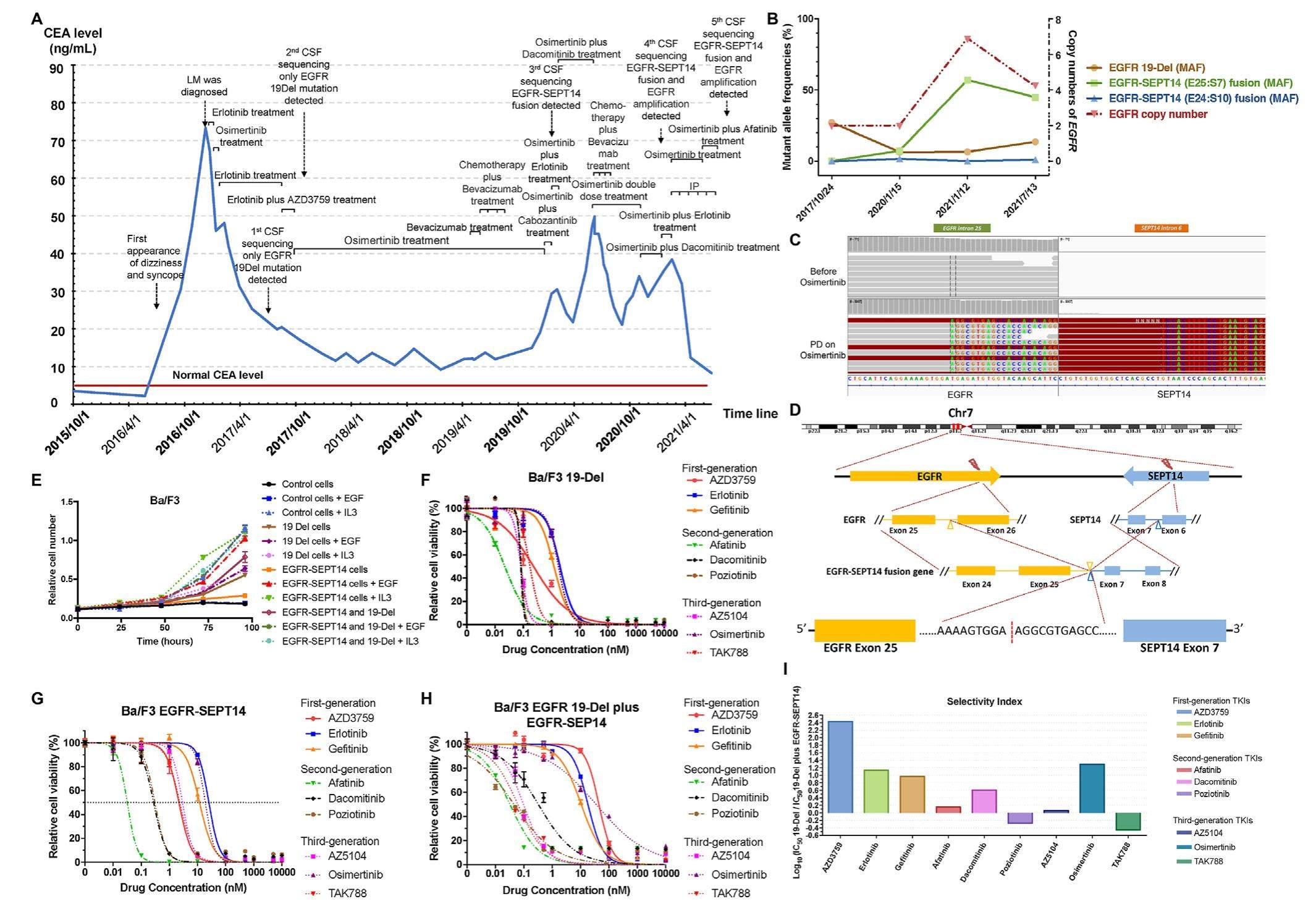
A novel acquired EGFR-SEPT14 fusion confers differential drug resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung adenocarcinoma


Around 10%-30% of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients harbored epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, with L858R and exon-19 deletions (19-Del) accounting for 90% of cases. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) showed significant efficacy against common EGFR mutations. However, the therapeutic relevance of uncommon EGFR mutations remained insufficiently investigated. EGFR fusions are extremely rare (0.05%-0.13%) in NSCLC, and Konduri group reported only 5 EGFR fusions from 10, 097 patients. Additional EGFR fusions were reported in NSCLC, all of which were oncogenic drivers and sensitive to EGFR TKIs. Herein, we reported an NSCLC patient with leptomeningeal metastasis (LM) who acquired a novel EGFR-SEPT14 fusion during TKI resistance and showed promising responses to certain EGFR TKIs and intrathecal pemetrexed (IP).