Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) H19: An essential developmental regulator with expanding roles in cancer, stem cell differentiation, and metabolic diseases


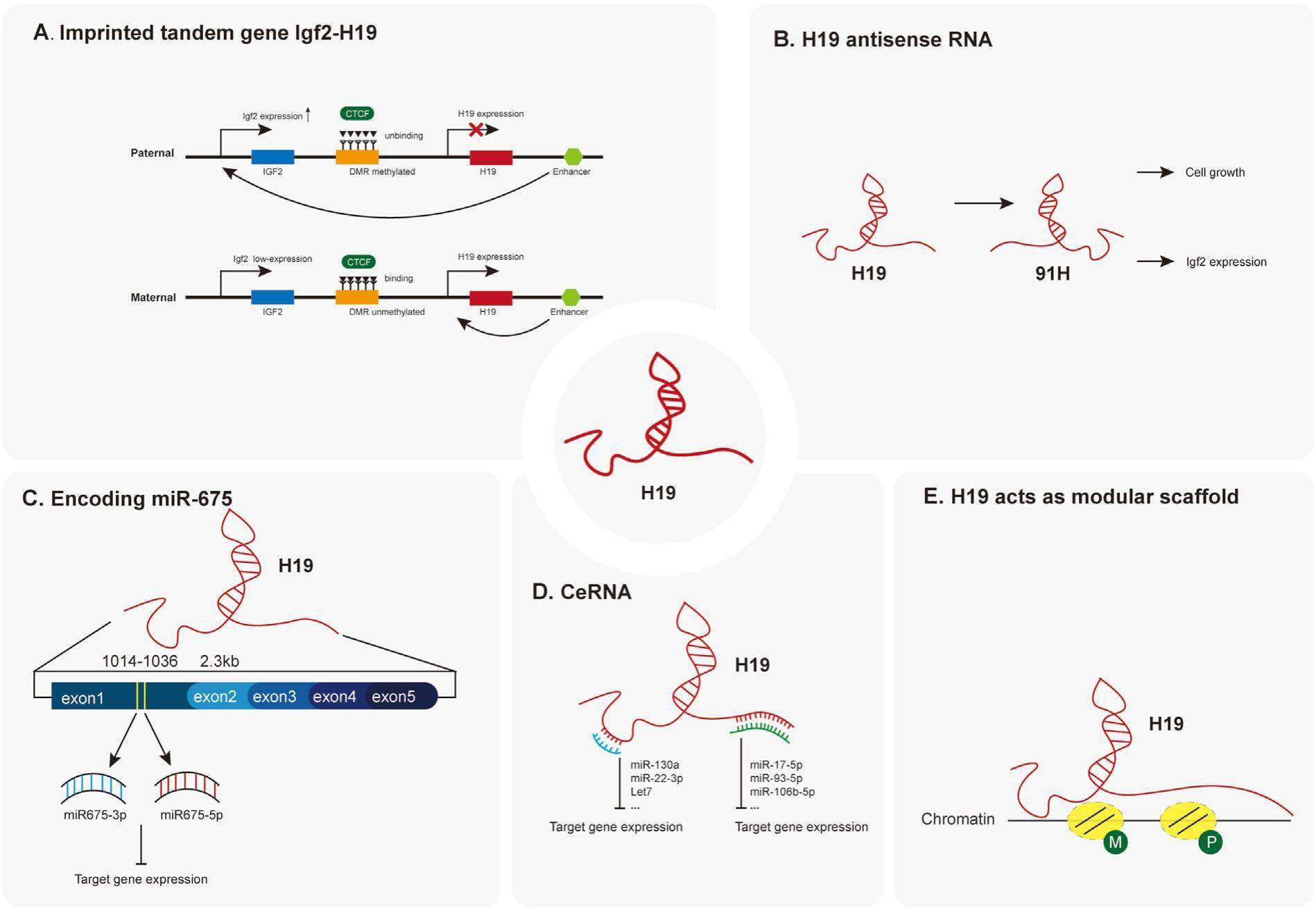
Recent advances in deep sequencing technologies have revealed that, while less than 2% of the human genome is transcribed into mRNA for protein synthesis, over 80% of the genome is transcribed, leading to the production of large amounts of noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs). It has been shown that ncRNAs, especially long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), may play crucial regulatory roles in gene expression. As one of the first isolated and reported lncRNAs, H19 has gained much attention due to its essential roles in regulating many physiological and/or pathological processes including embryogenesis, development, tumorigenesis, osteogenesis, and metabolism. Mechanistically, H19 mediates diverse regulatory functions by serving as competing endogenous RNAs (CeRNAs), Igf2/H19 imprinted tandem gene, modular scaffold, cooperating with H19 antisense, and acting directly with other mRNAs or lncRNAs. Here, we summarized the current understanding of H19 in embryogenesis and development, cancer development and progression, mesenchymal stem cell lineage-specific differentiation, and metabolic diseases. We discussed the potential regulatory mechanisms underlying H19's functions in those processes although more in-depth studies are warranted to delineate the exact molecular, cellular, epigenetic, and genomic regulatory mechanisms underlying the physiological and pathological roles of H19.Ultimately, these lines of investigation may lead to the development of novel therapeutics for human diseases by exploiting H19 functions.