IL-13/IL-13RA2 signaling promotes colorectal cancer stem cell tumorigenesis by inducing ubiquitinated degradation of p53


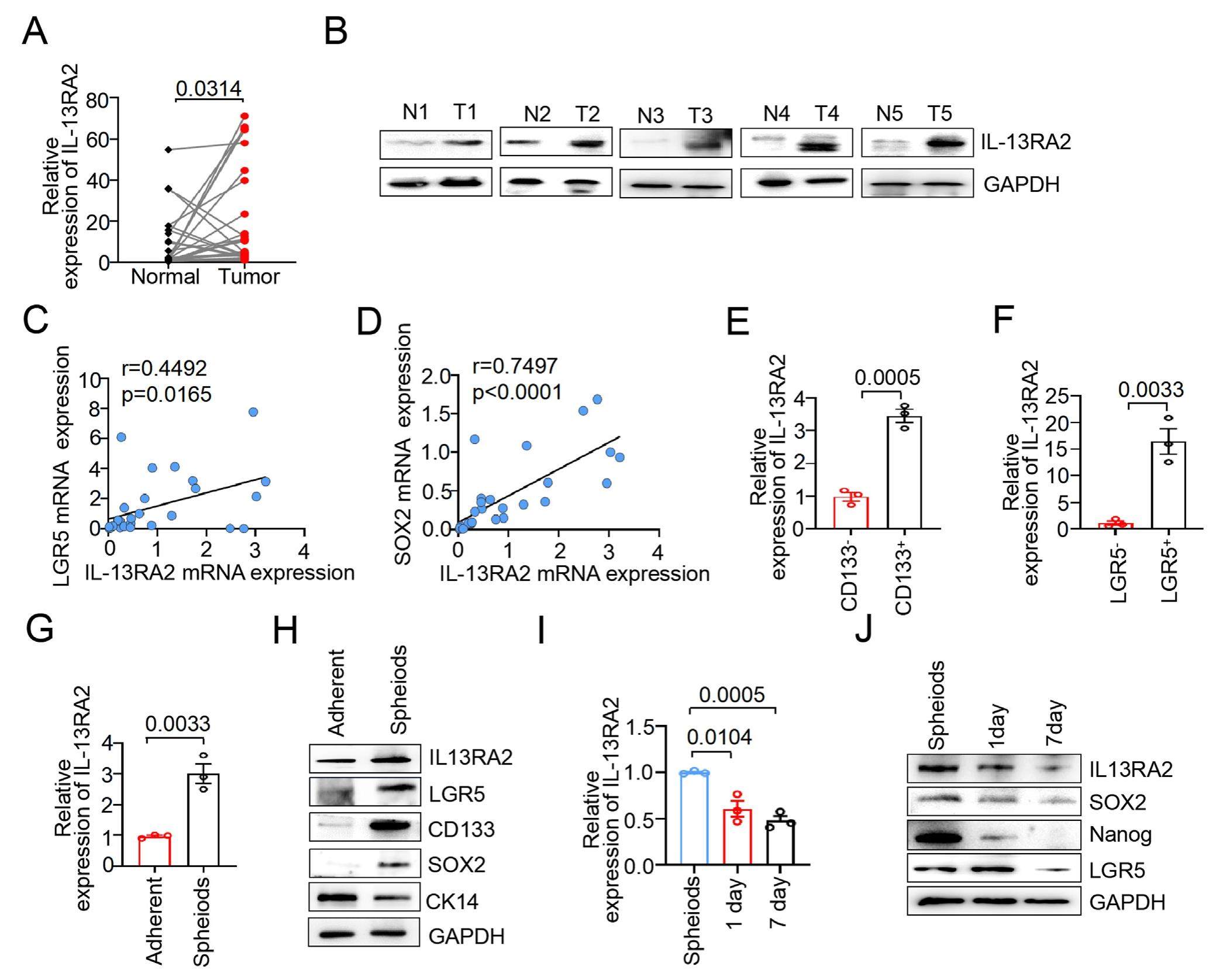
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are considered tumor-initiating cells and the main drivers of disease progression. Targeting these rare cancer cells, however, remains challenging with respect to therapeutic benefit. Here, we report the up-regulation of IL-13RA2 expression in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues and spheroid cells. The expression of IL-13RA2 was positively correlated with canonical stemness markers in CRC. We further demonstrated that the level of IL-13 was up-regulated in the serum of CRC patients. Biologically, recombinant IL-13 (rIL-13) stimulation promoted the sphere formation, proliferation, and migration of CRC cells in vitro and enhanced tumorigenesis in vivo. This phenotype could be reversed by knocking down IL-13RA2. Mechanistically, IL-13 activated autophagy by inducing LC3I/LC3II transformation in CRC-CSCs, which was crucial for the biological functions of IL-13. We further demonstrated that IL-13RA2 acted as a modular link of the E3 ligase UBE3C and the substrate p53 protein, enhancing the interaction of UBE3C and p53, thereby inducing the K48-linked ubiquitination of p53. In conclusion, the IL-13/IL-13RA2 signaling cascade promotes CRC-CSC self-renewal and tumorigenesis by inducing p53 ubiquitination, adding an important layer to the connection between IL-13 and p53, which can be translated into novel targeted therapies.