Rare variant analysis of PLXNA1 in Parkinson's disease in the Chinese population


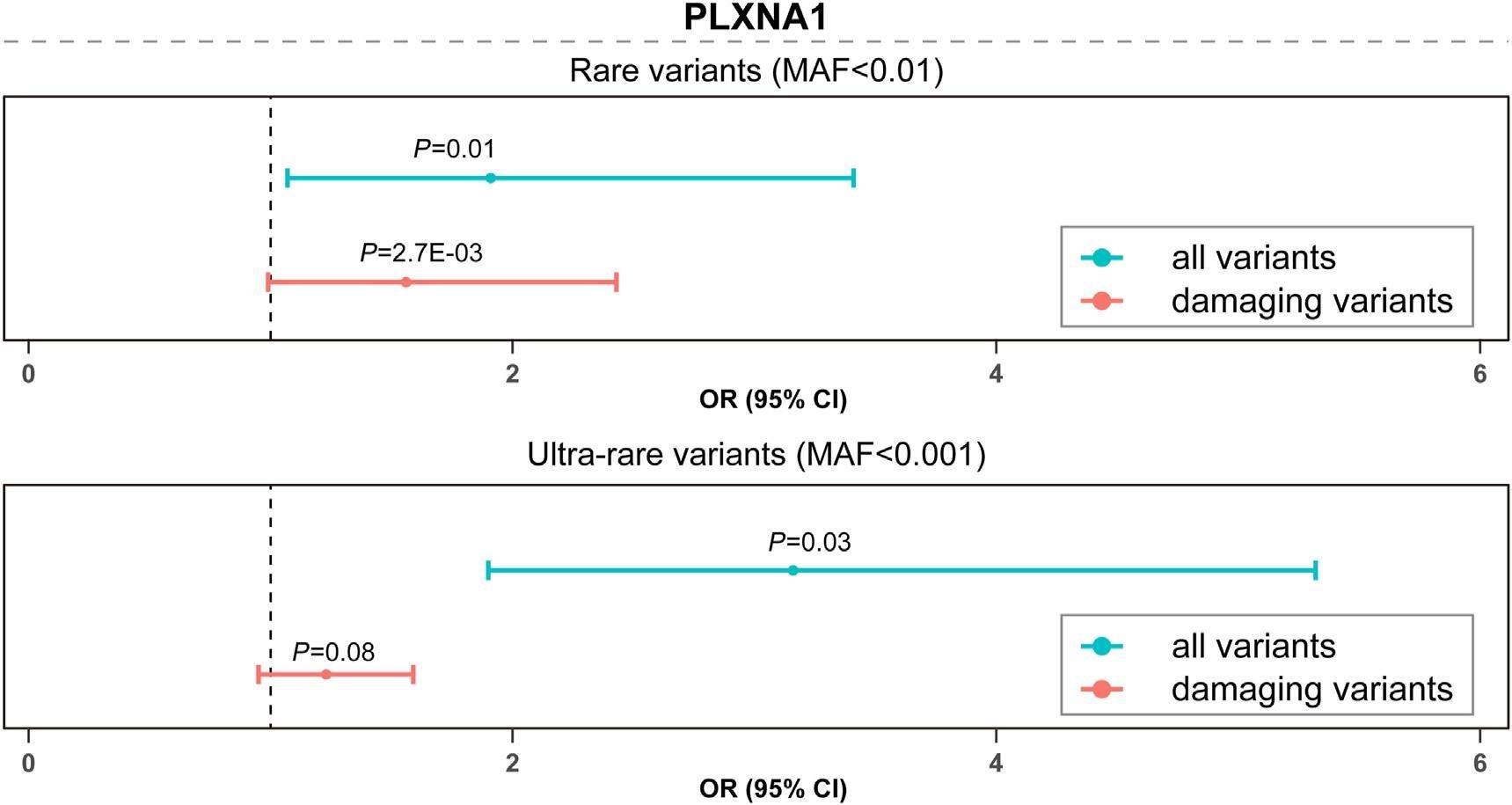
Recently, p. Glu1121Ter in PLXNA1 was identified as potential cause for a patient with parkinsonism. However, no further replication has been conducted in a wider range of Parkinson's disease (PD) cohorts. To evaluate the genetic association of PLXNA1 with PD, we systematically analyzed the rare protein-coding variants in 1,245 Chinese patients with whole exome sequencing. Fisher's exact test was performed between each variant and the risk of PD, while over-representation of rare variants in patients was examined with optimized sequence kernel association test at gene level. Totally, 42 rare variants were identified. At variant level, p. V172M was significantly associated with PD, while p. L12M and p. R571C were nominally associated with PD. Burden analysis showed enrichment of ultra-rare variants of PLXNA1 in PD.In addition, one patient carried a variant in the neighboring amino acid, and diaplayed clinical characteristics similar to those of the patient in the original study. Our study explored the rare variant of PLXNA1 in PD in the Asian population and paved the way for future research.