Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1A suppresses innate immune response by inducing degradation of TBK1 to inhibit steatohepatitis


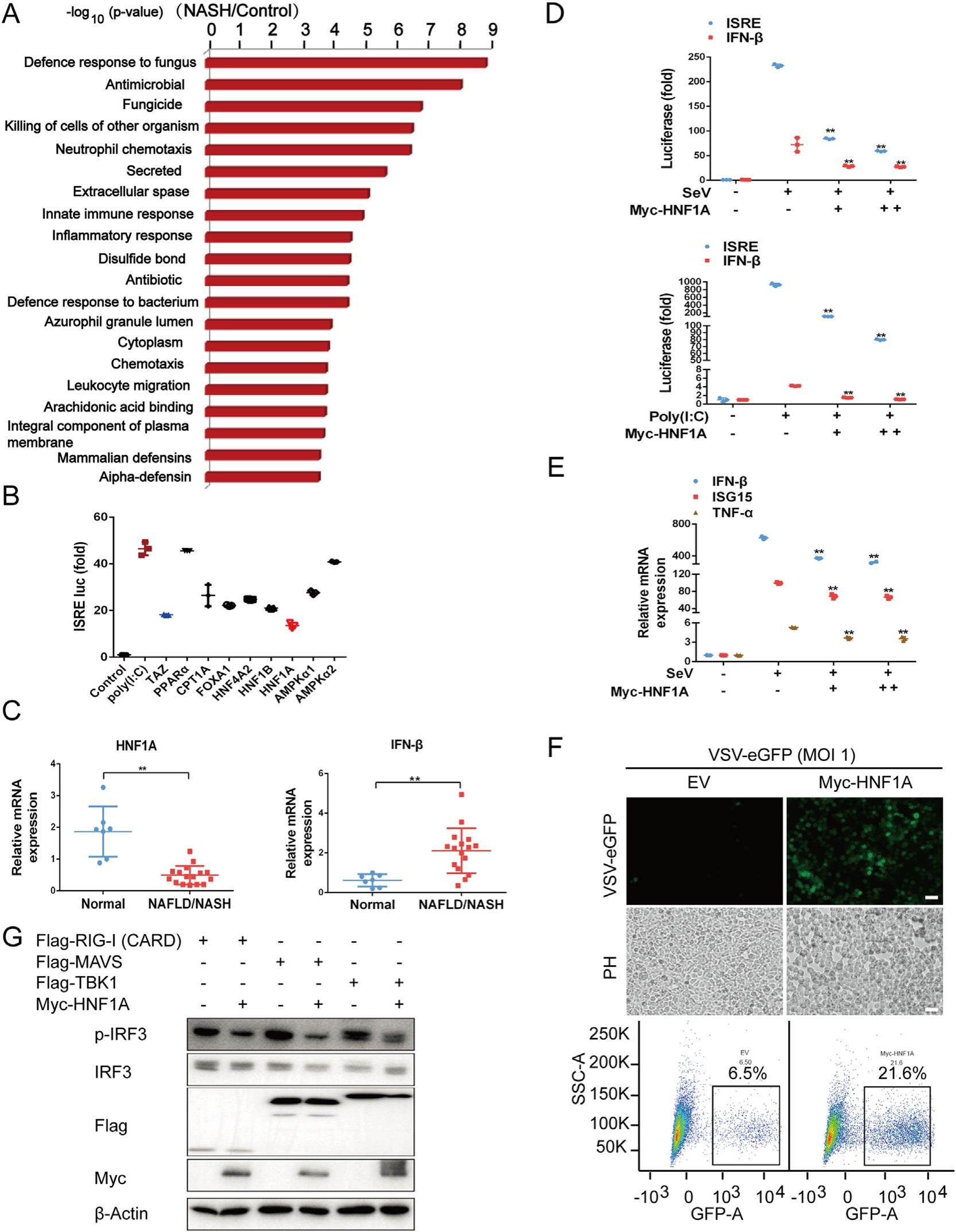
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a progressive form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is characterised by chronic liver inflammation, which can further progress into complications such as liver cirrhosis and NASH-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and therefore has become a growing health problem worldwide. The type I interferon (IFN) signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in chronic inflammation; however, the molecular mechanisms underlying NAFLD/NASH from the perspective of innate immune response has not yet been fully explored. In this study, we elucidated the mechanisms of how innate immune response modulates NAFLD/NASH pathogenesis, and demonstrated that hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha (HNF1A) was suppressed and the type I IFN production pathway was activated in liver tissues of patients with NAFLD/NASH. Further experiments suggested that HNF1A negatively regulates the TBK1-IRF3 signaling pathway by promoting autophagic degradation of phosphorylated-TBK1, which constrains IFN production, thereby inhibiting the activation of type I IFN signaling. Mechanistically, HNF1A interacts with the phagophore membrane protein LC3 through its LIR-docking sites, and mutations of LIRs (LIR2, LIR3, LIR4, and LIRs) block the HNF1A-LC3 interaction. In addition, HNF1A was identified not only as a novel autophagic cargo receptor but also to specifically induce K33-linked ubiquitin chains on TBK1 at Lys670, thereby resulting in autophagic degradation of TBK1.Collectively, our study illustrates the crucial function of the HNF1A-TBK1 signaling axis in NAFLD/NASH pathogenesis via crosstalk between autophagy and innate immunity.